Project Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<p id="Project-Management-Basics"> </p> | <p id="Project-Management-Basics"> </p> | ||
Image:Project-management-basics.jpg|left| | [[Image:Project-management-basics.jpg|left|thumb|699px|alt=Project management basics: What is project management - project management roles, project management stages and templates / checklists.|link=https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/File:Project-management-basics.jpg|[[#Project-Management-Basics|Project Management Basics]]]] | ||
<br style="clear:both;"/> | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 128: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | {| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="3" style="vertical-align:top; background:# | | colspan="3" style="vertical-align:top; text-align:center; background:#013b5e; color:#ffffff; font-size: 110%;" | <b>Operational organization of project processes</b> <br />Project stages: objectives and tasks<br /> | ||
|- | |- | ||
!style="background:# | !style="background:#facc6a; width: 20%; text-align:center" | Project stage | ||
!style="background:# | !style="background:#facc6a; width: 40%; text-align:center" | Objectives | ||
!style="background:# | !style="background:#facc6a; vertical-align:top; text-align:center" | Tasks | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project | |style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project initi­ation''' | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | | |style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
*Project goal is identified | *Project goal is identified | ||
| Line 148: | Line 141: | ||
| | | | ||
*Clarify | *Clarify assign­ments and tasks | ||
*Perform cost | *Perform cost assess­ment | ||
*Carry out risk and PESTLE analysis (P= | *Carry out risk and PESTLE analysis (P=Politi­cal, E=Econo­mic, S=Socio­logical, T=Techno­logical, L=Legal, E=Environ­mental) | ||
*Set-up rough project planning | *Set-up rough project planning | ||
*Build up project | *Build up project organi­zation | ||
*Hold kick-off meeting | *Hold kick-off meeting | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project | |style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project plan­ning''' | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | | |style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
*Work packages are defined | *Work packages are defined | ||
* | *Founda­tions for success­ful completion of the project within the execu­tion phase are laid | ||
| | | | ||
*Define, | *Define, evalu­ate and assign work packages | ||
*Set up time schedule | *Set up time schedule | ||
*Establish cost schedule | *Establish cost schedule | ||
*Prepare the working | *Prepare the working environ­ment (project infra­structure) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project | |style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project execu­tion''' | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | | |style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
*Project | *Project out­comes are defined and approved | ||
| | | | ||
*Execute work packages | *Execute work packages | ||
*Carry out project | *Carry out project con­trolling | ||
* | *Conti­nuous risk and quality manage­ment | ||
*Initiate and co-ordinate project changes, as | *Initiate and co-ordinate project changes, as re­quired | ||
*Carry out the | *Carry out the tech­nical accep­tance | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project closure''' | |style="vertical-align:top;" | '''Project closure''' | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | | |style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
*Critical project | *Critical project retro­spective (dates, costs, project develop­ment) is done | ||
*Project organization is | *Project organization is dis­solved | ||
*Project is formally completed | *Project is formally completed | ||
|style="vertical-align:top;" | | |style="vertical-align:top;" | | ||
*Prepare end project report | *Prepare end project report | ||
*Final | *Final presen­tation | ||
*Hand over and assure results | *Hand over and assure results | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 198: | Line 191: | ||
The following three project management standards have been accepted worldwide: | The following three project management standards have been accepted worldwide: | ||
*Project Management Body of Knowledge ([ | *Project Management Body of Knowledge ([https://www.pmi.org/pmbok-guide-standards PMBOK]), Project Management Institute (PMI), | ||
*PRojects IN Controlled Environments ( | *PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2), a standard which, like [[ITIL Processes|ITIL]], was developed by the Office of Government Commerce (OGC) | ||
*the IPMA Competence Baseline ([ | *the IPMA Competence Baseline ([https://www.ipma.world/individuals/standard/ ICB]) of the International Project Management Association (IPMA). | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
[1] John S Stewart. "[ | [1] John S Stewart. "[https://internationalbestpracticeinstitute.wordpress.com/2013/02/22/quick-guide-to-prince2/ Quick Guide to PRINCE2®]". -- Blog IBPI (The International Best Practice Institute) www.ibpi.org, February 22, 2013. Retrieved February 27, 2013. | ||
[2] Axelos - Global Best Practice. "[http://www.axelos.com/Knowledge-Centre/White-Papers/#GEMS6541916 PRINCE2® Introductory Overview and Business Benefits White Papers]"; "[http://www.axelos.com/Knowledge-Centre/White-Papers/#GEMS6541875 PRINCE2® Technical White Papers]". -- Axelos, www.axelos.com. Retrieved January 29, 2014. | [2] Axelos - Global Best Practice. "[http://www.axelos.com/Knowledge-Centre/White-Papers/#GEMS6541916 PRINCE2® Introductory Overview and Business Benefits White Papers]"; "[http://www.axelos.com/Knowledge-Centre/White-Papers/#GEMS6541875 PRINCE2® Technical White Papers]". -- Axelos, www.axelos.com. Retrieved January 29, 2014. | ||
| Line 211: | Line 204: | ||
→ Proceed to: [[Project Management - Templates, Checklists and Tips|Templates, checklists and tips for project management]] | → Proceed to: [[Project Management - Templates, Checklists and Tips|Templates, checklists and tips for project management]] | ||
<p> </p> | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 244: | Line 238: | ||
<meta itemprop="Headline" content="Project Management" /> | <meta itemprop="Headline" content="Project Management" /> | ||
<link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/d/d1/Project-management-basics.jpg" /> | <link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/d/d1/Project-management-basics.jpg" /> | ||
<link itemprop="author" href="https:// | <link itemprop="author" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/andreakempter" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="author" content="Andrea Kempter" /> | <meta itemprop="author" content="Andrea Kempter" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="creator copyrightHolder publisher" content="IT Process Maps" /> | <meta itemprop="creator copyrightHolder publisher" content="IT Process Maps" /> | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 28 July 2021


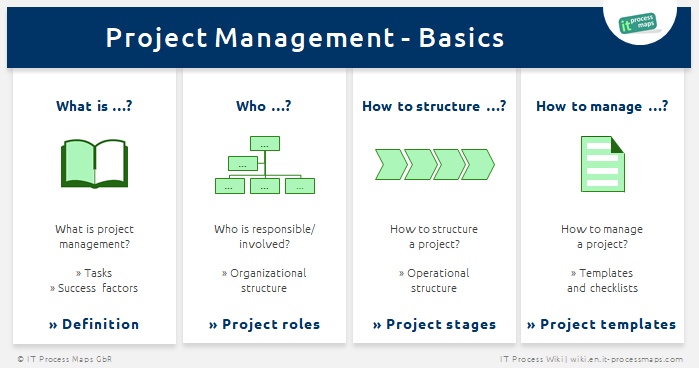
In recent years, project management has become more and more important. The reason is that very often for modern enterprises it is vital to respond quickly and flexibly to new requirements.
What is Project Management?
When a business has to address a completely new task it is usually necessary that specialists from very different areas and corporate sectors work together. Here the definition of a project would make sense: It ensures a higher degree of flexibility as it goes beyond day-to-day operations. Project work provides the benefit of finding common solutions rapidly and effectively.
On the other hand, success of the project is not guaranteed, since its content is always new, contrary to business operations which are repetitive and have long been practiced in the company. Even when several approaches have been developed to achieve the project goal, the result is often incalculable.
For these reasons, it is essential to have access to reliable project planning, concrete commitment of the necessary resources and, most important, clear rules for the project work (see: templates, checklists and tips for project management).
All these activities are summarized under the term "Project management":
Project management encompasses organization, planning, control and monitoring of all tasks and resources required to achieve the defined project goals and objectives.
Project management is a managerial task and must be distinguished from the practical tasks of the operational project work.
What is a Project?
Frequently, a task is misleadingly classified as a "project". As a rule, the following general conditions should be fulfilled for tasks to be completed in the form of a project:
The task
- is unique, i.e. no routine task to be completed as part of the day-to-day operational business,
- is a novelty,
- is subject to constraints by timescale, funding and staff,
- has a complex technical and organizational structure,
- has clear performance targets with regard to the agreed specification and quality,
- is implemented in teamwork, generally by cross-disciplinary and cross-hierarchy project teams.
Success Factors
A project can be considered "successful" if the output as defined in the project order has been delivered within the scheduled time frame and budgets and with the planned resources.
But careful: Due to the fact that a project is unique and complex, it also bears the risk of not yielding the desired results.
However, the risk of failing can be considerably reduced through rigorous project management ensuring that
- the various people involved act in a co-ordinated way,
- the complexity of the tasks is reduced through structuring,
- the project contents are subdivided into meaningful units to ensure clarity and ease of handling,
- the goals are achieved and
- neither deadlines nor financial limits are exceeded.
Ultimately, very different factors contribute to the success of a project. These factors range from technical issues to organizational agreements and interpersonal aspects.
Project Organization
So as we can see from the above, a project cannot be executed as part of the usual day-to-day business, but has its own rules.
An appropriate project organization helps minimize frictional losses and delays in the project.
It serves to
- assign authority, tasks and responsibilities clearly,
- manage the co-operation, communication and co-ordination of all people involved in the project,
- ensure rapid response to changes in the general conditions or the project goals and objectives.
Organizational Structure (Definition of Project Tasks and Responsibilities)
When it comes to multidisciplinary and multi-department teams working together on individual tasks for a limited period of time, it is essential that the organizational structures in the company are flexible, e.g. to allow direct co-operation between specialists. The inclusion of people from different areas of expertise, organizational structures and hierarchical levels raises the issue of clearly defined project responsibilities. Moreover, a rapid flow of information and close communication is required.
When working together on the successful completion of a project, it is therefore necessary to determine right from the beginning who will participate in the project. It must be defined what their respective functions, responsibilities and competencies will be. Likewise, the information flow between the members of the project team must be determined.
Communication within the project team is often taken for granted; people tend to assume that this will function more or less automatically. However, guidelines may be helpful, here too, and may in the long run help to considerably reduce the amount of time which the members of the project team invest in the project.
It has proved useful to define distinct tasks and responsibilities, i.e. project roles in an organizational structure:
- The executive is the person or group of persons who allocates funding to the project. He is the key decision-maker and is ultimately responsible for the success of the project.
- The project board (often referred to as Steering Committee) represents the executive and, as the highest-level body, is responsible for providing guidance on the overall strategic direction of the project. It makes the most important decisions with regard to the goal and the scope of the project.
- The project manager is responsible for the operational management of the project.
- The project team is in charge of the technical project work.
Operational Structure (Planning of the Project Structure)
It is proven practice to break down the project cycle into different stages. It is a planning approach that provides the possibility of obtaining measurable interim results during project execution, thus lowering the project risks considerably. Moreover, it is much easier to discuss and decide on the course to be set for the project if data regarding milestone results and deviations from plans are available.
The aim of stage planning is to make the project progress transparent.
Project Stages: Objectives and Tasks
| Operational organization of project processes Project stages: objectives and tasks | ||
| Project stage | Objectives | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Project initiation |
|
|
| Project planning |
|
|
| Project execution |
|
|
| Project closure |
|
|
Project Management Standards
The following three project management standards have been accepted worldwide:
- Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), Project Management Institute (PMI),
- PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2), a standard which, like ITIL, was developed by the Office of Government Commerce (OGC)
- the IPMA Competence Baseline (ICB) of the International Project Management Association (IPMA).
Links
[1] John S Stewart. "Quick Guide to PRINCE2®". -- Blog IBPI (The International Best Practice Institute) www.ibpi.org, February 22, 2013. Retrieved February 27, 2013.
[2] Axelos - Global Best Practice. "PRINCE2® Introductory Overview and Business Benefits White Papers"; "PRINCE2® Technical White Papers". -- Axelos, www.axelos.com. Retrieved January 29, 2014.
IT Process Wiki: Project Management Templates
→ Proceed to: Templates, checklists and tips for project management
Notes
By: Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Definition › Success factors › Project organization › Project stages › PM templates






