ITIL 4


ITIL 4 - the most recent release of ITIL® [1] - was launched in February 2019. It's the first major update to the ITIL framework since 2007, designed in large part to keep up with recent trends in software development and IT operations.
On this page we answer your questions about the changes introduced with the latest edition of ITIL (see fig. 1: ITIL 4 FAQs).
Objectives
- ITIL 4 provides a flexible foundation for organizations that need to integrate various frameworks and approaches into their service management operating models.
- ITIL 4 aims to help businesses navigate the new technological era of digital services.
Why ITIL 4?
ITIL 4 brings the ITIL framework up to date, introducing a holistic approach to service management and focusing on 'end-to-end service management from demand to value'.
The new edition of ITIL 4 is the first major update to ITIL since 2007 and is arguably a response to the emergence of newer service management frameworks such as VeriSM™, SIAM® and FitSM. It expands the previous version of ITIL V3 ('ITIL 2011') and provides a flexible basis to support organizations on their journey to the new world of digital transformation.
ITIL 4 describes an operating model for the delivery of tech-enabled products and services. The documentation has been completely revised and streamlined to make it easier to read, and enhanced with many practical examples.
ITIL 4 also reflects recent trends in software development and IT operations, and includes advice on how to apply philosophies such as Agile, DevOps and Lean in the domain of service management.
Last but not least, ITIL 4 makes a point of being "a framework for service management" (as opposed to "IT service management"), reflecting the growing trend of applying service management best practices in the domain of enterprise and business services.
ITIL 4 components
ITIL 4 consists of two key components:
Four dimensions model
ITIL 4 defines four dimensions that should be considered to ensure a holistic approach to service management:
- Organizations and people
- Information and technology
- Partners and suppliers
- Value streams and processes.
These dimensions are applicable to the service value system in general and to specific services.
Service value system
The service value System (SVS) represents "how all the components and activities of an organization work together to facilitate value creation". The ITIL 4 SVS includes several elements:
- Guiding principles
- Governance
- Service value chain
- Continual improvement
- Practices.
ITIL 4 management practices
ITIL 4 includes 34 management practices as "sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective". For each practice, ITIL 4 provides various types of guidance, such as key terms and concepts, success factors, key activities, information objects, etc.
The 34 ITIL 4 practices are grouped into three categories:
General management practices
The ITIL 4 general management practices include:
- Strategy management
- Portfolio management
- Architecture management
- Service financial management
- Workforce and talent management
- Continual improvement
- Measurement and reporting
- Risk management
- Information security management
- Knowledge management
- Organizational change management
- Project management
- Relationship management
- Supplier management
Service management practices
The service management practices in ITIL 4 include:
- Business analysis
- Service catalogue management
- Service design
- Service level management
- Availability management
- Capacity and performance management
- Service continuity management
- Monitoring and event management
- Service desk
- Incident management
- Service request management
- Problem management
- Release management
- Change enablement
- Service validation and testing
- Service configuration management
- IT asset management
Technical management practices
The ITIL 4 technical management practices include:
- Deployment management
- Infrastructure and platform management
- Software development and management
ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: What's the difference?
ITIL 4 is not about introducing new fundamental ideas of service management and should be seen as an expansion of the time-tested ITIL framework, not a replacement. Essentially, ITIL 4 and ITIL V3 provide guidance based on the same underlying principles, but ITIL 4 takes a new approach to presenting this guidance.
ITIL V3 contains detailed descriptions of 26 ITIL processes, arranged along the service lifecycle:
The service lifecycle has been dropped in ITIL 4 and the processes replaced with practices. But many of the ITIL 4 practices clearly correspond to the previous ITIL V3 processes.
Other than that, ITIL 4 introduces additional guidance, to ensure practitioners better understand the core principles and concepts such as "value" and "outcomes".
ITIL 4 also provides advice for integrating ITIL with other frameworks and methodologies like DevOps, Lean and Agile.
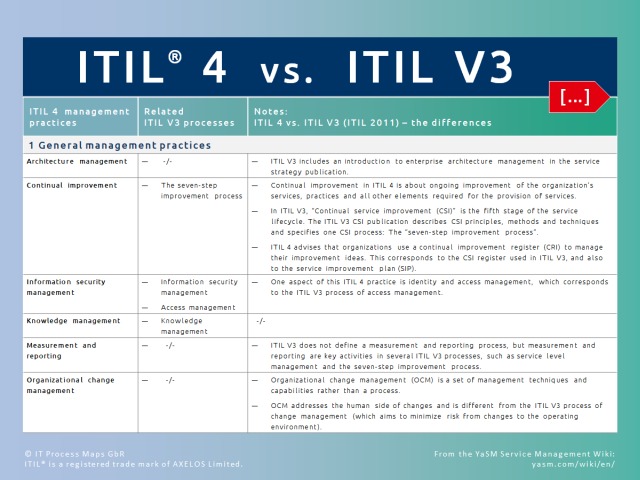
(in our YaSM® Service Management Wiki)
Learn more about the differences between ITIL 4 and ITIL V3 (ITIL 2011) in our YaSM Service Management Wiki.
What about ITIL 4 processes?
While ITIL V3 defined a set of processes organized around the service lifecycle, ITIL 4 describes principles, concepts and practices. This includes key activities and essential inputs and outputs for each practice, but not detailed process specifications. This departure from the previous process-oriented approach is a fundamental change in ITIL 4 that enables service providers to adopt more flexible operating models.
ITIL 4 is thus not prescriptive regarding processes. But organizations still need to define their processes as a key element of their operating models (ITIL 4 says that "organizations should define tailor-made processes", in line with their specific requirements).
Organizations looking for detailed process descriptions can still find them in the ITIL V3 publications (AXELOS state that ITIL 4 does not invalidate earlier vesions of ITIL, and the processes as specified in ITIL V3 are therefore still valid guidance).
But the arrival of ITIL 4 and its preference for "simple and practical" ways of working also provides an opportunity for a fresh start with service management processes.
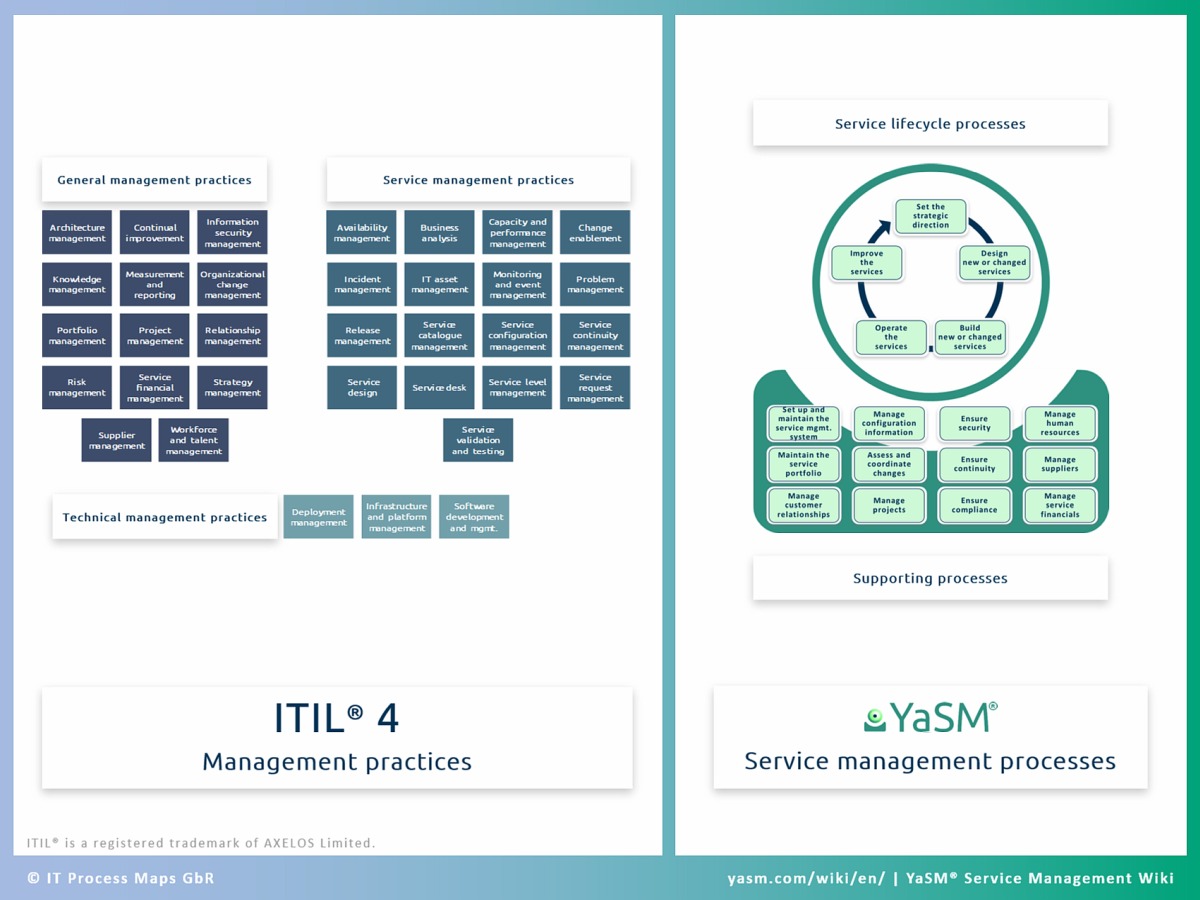
(in our YaSM® Service Management Wiki)
If organizations are to keep things simple and become more agile, they will likely need processes that are somewhat less complex than the 26 service management processes familiar from ITIL V3.
In the YaSM Service Management Wiki [2] we describe such a streamlined, clear-cut set of service management processes that is a good match for the leaner, more flexible operating models favored by today's service provider organizations.
The benchmark for the YaSM processes is ISO 20000 (ISO 20000:2018), the international standard for service management.
What is more, these service management processes are designed to be used with a variety of frameworks and methods, such as
ITIL 4 and ISO 20000, SIAM, VeriSM, ...
ITIL is some 30 years old and over the years has been adopted by a large number of organizations. It has been updated from time to time, but other, newer service management frameworks and approaches have been quicker in recognizing emerging trends in service management and information technology. ITIL 4 has arguably taken a leaf or two out of these frameworks to keep up with the times. Here are a few examples:
- ITIL 4 includes updated guidance on multi-sourcing and service integration. These are key topics in the SIAM® framework.
- ITIL 4 embraces new ways of working, such as Agile, Lean and DevOps, as well as organizational change management. These management practices and their relevance for service management are also described in the VeriSM™ approach.
- The ITIL 4 service value chain is somewhat reminiscent of the VeriSM™ model, with key areas such as define, produce, provide and respond.
- ITIL 4 introduces the concept of a service value system. This fits in with a key requirement in the latest edition of ISO 20000 (ISO 20000:2018) for organizations to "establish, implement, maintain and continually improve" a service management system.
ITIL 4 certification scheme
What are the ITIL 4 certification levels?
ITIL 4 introduces a completely new, "streamlined" certification scheme.
- As in ITIL V3, Foundation is the entry level ITIL 4 certification, introducing the key elements, concepts and terminology used in ITIL.
- After passing the Foundation exam, ITIL practitioners can choose between two major ITIL certification "streams", each consisting of several modules: ITIL Managing Professional (MP) and ITIL Strategic Leader (SL).
- The ITIL 4 Managing Professional (ITIL MP) stream provides the "essential skills to run successful IT-enabled products and services". ITIL MP consists of four modules:
- ITIL 4 Strategist: Direct Plan and Improve (DPI)
- ITIL 4 Specialist: High Velocity IT (HVIT)
- ITIL 4 Specialist :Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV)
- ITIL 4 Specialist: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS).
- The ITIL 4 Strategic Leader (ITIL SL) stream "helps established and aspiring IT leaders to navigate the complexities of the digital era and prepare for digital transformation". ITIL SL consists of two modules:
- ITIL 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI)
- ITIL 4 Leader: Digital and IT Strategy (DITS).
- ITIL 4 Extension Modules is a stream of four modules providing "guidance to address and harness the challenges and opportunities presented by emerging technologies". The four modules are:
- ITIL 4 Specialist: Sustainability in Digital & IT
- ITIL 4 Specialist: Acquiring & Managing Cloud Services
- ITIL 4 Specialist: Business Relationship Management
- ITIL 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management.
- ITIL 4 Practice Manager Certifications (PM) is a stream consisting of practice-based modules.
- ITIL 4 PM provides shorter and more flexible training with opportunity to bundle, mix and match the modules. Each module focuses on one of the ITIL management practices, representing some of the most practical resources of the framework.
- In addition to completing five individual practices, succesful candidates will also need to complete the ITIL Specialist: Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) module.
- ITIL Master is the top-level qualification of the ITIL 4 certification scheme.
Successful candidates must have completed the Practice Manager (PM), Managing Professional (MP) and Strategic Leader (SL) streams. Certification will be provided upon successful completion of these streams. There is no need to apply.
More information about the new ITIL 4 certification scheme is available on the AXELOS website: [1].
Will my certifications stay valid?
ITIL V3 certifications will remain valid, but pressure to upgrade to the latest certifications is likely to grow. This is particularly true for ITSM consultants, whose customers will often expect up-to-date qualifications.
For those who wish to migrate to the new ITIL 4 certification scheme, AXELOS have prepared a transition plan:
How can I migrate to the new ITIL 4 certifications?
Holders of ITIL V3 Foundation certificates:
- There are significant changes in the ITIL 4 Foundation material.
- AXELOS advise candidates who have taken the ITIL V3 Foundation exam to take ITIL 4 Foundation in order to be able to transition to the new scheme.
Holders of ITIL V3 Intermediate or Practitioner certifications:
- The best migration path towards the ITIL 4 scheme will depend on the number of credits already earned.
- Candidates may either choose to restart their certification itinerary with ITIL 4 Foundation, or to complete ITIL V3 Expert and then take the ITIL 4 Managing Professional Transition module.
Holders of ITIL V3 Expert certifications:
- Candidates who have achieved ITIL V3 Expert will be able to take the ITIL Managing Professional Transition module to achieve the ITIL Managing Professional designation.
Notes
[1] ITIL® is a registered trademark of the PeopleCert group.
[2] YaSM® is a registered trademark of IT Process Maps GbR.
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Objectives › Why ITIL 4? › ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: Differences › What about ITIL 4 processes? › ITIL 4 certification scheme






