IT Service Continuity Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
;<span id="Test Report">Test Report</span> | ;<span id="Test Report">Test Report</span> | ||
:A | :A Test Report provides a summary of testing and assessment activities. A Test Report is created for example during Release tests in the Service Transition stage or during tests carried out by [[Availability Management|Availability]], [[IT Service Continuity Management|IT Service Continuity]] or [[IT Security Management|Information Security Management]]. | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
| align="left" |[[#Service Continuity|Design Services for Continuity]] | | align="left" |[[#Service Continuity|Design Services for Continuity]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R | | R | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| R | | R | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" |[[#IT Service Continuity Review|ITSCM Review]] | | align="left" |[[#IT Service Continuity Review|ITSCM Review]] | ||
Revision as of 17:06, 27 February 2012
<seo metakeywords="service continuity management, itil service continuity, itil service continuity management, itscm itil v3, service continuity itil, service continuity process" metadescription="IT Service Continuity Management: ITIL process definition - Sub-processes - Terms - Additional information on ITIL V3 ITSCM." />

Overview
Objective: IT Service Continuity Management (ITSCM) aims to manage risks that could seriously impact IT services. ITSCM ensures that the IT service provider can always provide minimum agreed Service Levels, by reducing the risk from disaster events to an acceptable level and planning for the recovery of IT services. ITSCM should be designed to support Business Continuity Management.
Part of: Service Design
Process Owner: IT Service Continuity Manager
Process Description
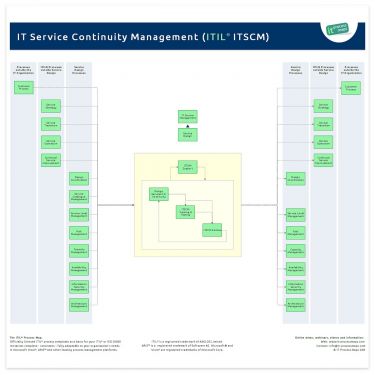
There are no major differences between IT Service Continuity Management in ITIL V3 (2007) and ITIL 2011.
Following the introduction of Design Coordination in ITIL 2011 the information flows have been adapted. The process overview of IT Service Continuity Management (.JPG) is showing the most important interfaces (see Figure 1).
Note: IT Service Continuity Management ensures that appropriate continuity mechanisms are in place. The recovery of IT services is managed through the Incident Management process, especially the "Handling of Major Incidents" sub-process.
Sub-Processes
These are the IT Service Continuity Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
- ITSCM Support
- Process Objective: To make sure that all members of IT staff with responsibilities for fighting disasters are aware of their exact duties, and to make sure that all relevant information is readily available when a disaster occurs.
- Design Services for Continuity
- Process Objective: To design appropriate and cost-justifiable continuity mechanisms and procedures to meet the agreed business continuity targets. This includes the design of risk reduction measures and recovery plans.
- ITSCM Training and Testing
- Process Objective: To make sure that all preventive measures and recovery mechanisms for the case of disaster events are subject to regular testing.
- ITSCM Review
- Process Objective: To review if disaster prevention measures are still in line with risk perceptions from the business side, and to verify if continuity measures and procedures are regularly maintained and tested.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in IT Service Continuity Management to represent process outputs and inputs:
- Availability/ ITSCM/ Security Testing Schedule
- A schedule for the regular testing of all availability, continuity and security mechanisms, jointly maintained by Availability, IT Service Continuity and Information Security Management.
- Business Continuity Strategy
- An outline of the approach to ensure the continuity of Vital Business Functions in the case of disaster events. The Business Continuity Strategy is prepared by the business and serves as a starting point for producing the IT Service Continuity Strategy.
- Disaster Recovery Invocation Guideline
- A document produced by IT Service Continuity Management with detailed instructions on when and how to invoke the procedure for fighting a disaster. Most importantly, the guideline defines the first steps to be taken by 1st Level Support after learning that a (suspected) disaster has occurred.
- Index of Disaster-Relevant Information
- A catalogue of all information that is relevant in the event of disasters. This document is maintained and circulated by IT Service Continuity Management to all members of IT staff with responsibilities for fighting disasters.
- IT Service Continuity Report
- The IT Service Continuity Report is created at regular intervals and provides other Service Management processes and IT Management with information related to disaster prevention.
- IT Service Continuity Plan
- IT Service Continuity Plans underpin the ITSCM Strategy, describing how continuity is ensured for specific disaster events and services. It specifies the measures to enhance the resilience of services and describes how to effectively respond to a disaster event. ITSCM Plans usually include references to more detailed Recovery Plans with specific instructions for returning systems to a working state.
- IT Service Continuity Strategy
- The IT Service Continuity Strategy contains an outline of the approach to ensure the continuity of vital services in the case of disaster events. It includes a list of Vital Business Functions and applied risk reduction or recovery options. The IT Service Continuity Strategy should be based on a Business Continuity Strategy. The ITSCM Strategy is underpinned by more detailed ITSCM Plans, describing how continuity is ensured for specific disaster events and services.
- Recovery Plan
- Recovery Plans are created mainly by Availability and IT Service Continuity Management. The plans contain detailed instructions for returning specific services and/or systems to a working state, which often includes recovering data to a known consistent state.
- Test Report
- A Test Report provides a summary of testing and assessment activities. A Test Report is created for example during Release tests in the Service Transition stage or during tests carried out by Availability, IT Service Continuity or Information Security Management.
Checklists | KPIs
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) IT Service Continuity Management
- Checklists IT Service Continuity Management:
Roles | Responsibilities
- IT Service Continuity Manager - Process Owner
- The IT Service Continuity Manager is responsible for managing risks that could seriously impact IT services.
- He ensures that the IT service provider can provide minimum agreed service levels in cases of disaster, by reducing the risk to an acceptable level and planning for the recovery of IT services.
| Responsibility Matrix: IT Service Continuity Management | |||||
| ITIL Role | Sub-Process | IT Service Continuity Manager | Service Owner[3] | Applications Analys[3] | Technical Analyst[3] | IT Operator[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITSCM Support | A[1]R[2] | ||||
| Design Services for Continuity | AR | R | R | R | |
| ITSCM Training and Testing | AR | R | |||
| ITSCM Review | AR | ||||
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the IT Service Continuity Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within ITIL Continuity Management.
[3] siehe → Role descriptions ...






