IT Security Management

Objective: Information Security Management aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of an organization's information, data and IT services. ITIL Security Management usually forms part of an organizational approach to security management which has a wider scope than the IT Service Provider.
Part of: Service Design
Process Owner: Information Security Manager
Process Description
ITIL V3 treats Information Security Management as part of the Service Design core volume, resulting in a better integration of this process into the Service Lifecycle (the previous ITIL version provided guidance on Security Management in a separate book).
The process has been updated to account for new information security concerns.
ITIL does not provide a detailed explanation of all aspects of Information Security Management, as there are dedicated and more detailed standards available (see, for example, ISO 27001). Rather, ITIL highlights the most important activities and assists in identifying interfaces with other Service Management processes.
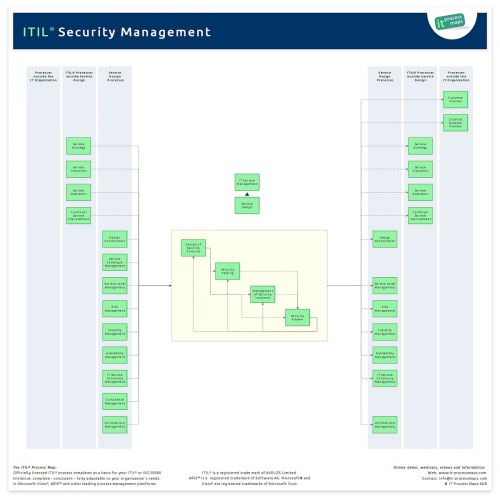
Following the introduction of Design Coordination in ITIL 2011 the information flows have been adapted. The process overview of ITIL Security Management (.JPG) shows the key information flows (see fig. 1).
ITIL 4 refers to 'Information Security Management' as a general management practice.
Sub-Processes
These are the Information Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
Design of Security Controls
- Process Objective: To design appropriate technical and organizational measures in order to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, security and availability of an organization's assets, information, data and services.
Security Testing
- Process Objective: To make sure that all security mechanisms are subject to regular testing.
Management of Security Incidents
- Process Objective: To detect and fight attacks and intrusions, and to minimize the damage incurred by security breaches.
Security Review
- Process Objective: To review if security measures and procedures are still in line with risk perceptions from the business side, and to verify if those measures and procedures are regularly maintained and tested.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in the Security Management process to represent process outputs and inputs:
Availability/ ITSCM/ Security Testing Schedule
- A schedule for the regular testing of all availability, continuity and security mechanisms, jointly maintained by Availability, IT Service Continuity and Information Security Management.
Event Filtering and Correlation Rules
- Rules and criteria used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring systems. Some of those rules are defined during the Service Design stage, for example to ensure that Events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered.
- Note: The output "Event Filtering and Correlation Rules" has been added in ITIL 2011, to emphasize that (some) Event filtering and correlation rules should be designed by Information Security Management to support the detection of security issues.
Information Security Policy
- The Information Security Management Policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing information security. It includes references to more specific Underpinning Information Security Policies which, for example, set binding rules for the use of systems and information.
Information Security Report
- The Information Security Report provides other Service Management processes and IT Management with information related to Information Security issues.
Security Advisories
- A list of known security vulnerabilities compiled from input by third-party product suppliers. The list contains instructions for preventive measures and for the handling of security breaches once they occur.
Security Alert
- A warning produced by Information Security Management, typically released when outbreaks of security threats are foreseeable or already under way. The aim is to make sure that users and IT staff are able to identify any attacks and take appropriate precautions.
Security Management Information System (SMIS)
- A virtual repository of all Information Security Management data, usually stored in multiple physical locations.
Test Report
- A Test Report provides a summary of testing and assessment activities. A Test Report is created for example during Release tests in the Service Transition stage or during tests carried out by Availability, IT Service Continuity or Information Security Management.
Underpinning Information Security Policy
- Underpinning Information Security Policies are specific policies complementing the main Information Security Policy by setting binding rules for the use of systems and information as well as for the use and delivery of services, with the aim of improving information security.
KPIs
Roles | Responsibilities
Information Security Manager - Process Owner
- The Information Security Manager is responsible for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and availability of an organization’s assets, information, data and IT services. He is usually involved in an organizational approach to Security Management which has a wider scope than the IT service provider, and includes handling of paper, building access, phone calls etc., for the entire organization.
| ITIL Role / Sub-Process | Information Security Manager | Service Owner[3] | Applications Analyst[3] | Technical Analyst[3] | IT Operator[3] | Facilities Manager[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design of Security Controls | A[1]R[2] | R | R | R | - | - |
| Security Testing | AR | - | - | - | R | R |
| Management of Security Incidents | AR | - | - | - | - | - |
| Security Review | AR | - | - | - | - | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Information Security Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within ITIL Security Management.
[3] siehe → Role descriptions ...
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Process Description › Sub-Processes › Definitions › Roles






