ITIL Service Operation


Objective: The objective of ITIL Service Operation is to make sure that IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently. The Service Operation lifecycle stage includes the fulfilling of user requests, resolving service failures, fixing problems, as well as carrying out routine operational tasks.
Part of: IT Service Management | ITIL processes
Processes: ITIL Service Operation
Service Operation carries out operational tasks.
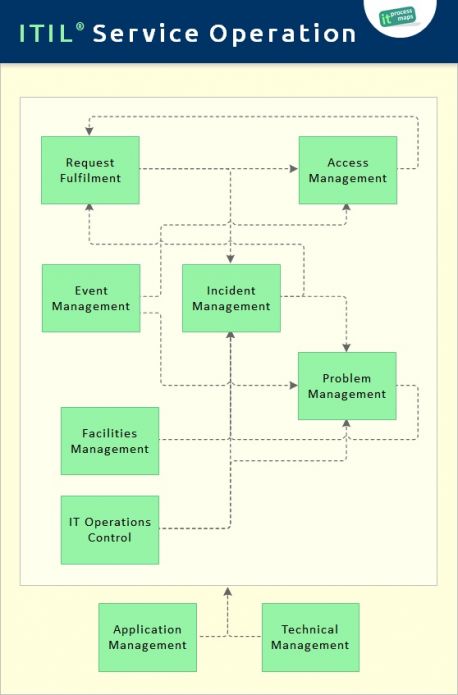
The ITIL service lifecycle stage of Service Operation (see fig. 1) includes the following main processes:
- Event Management
- Process Objective: To make sure CIs and services are constantly monitored, and to filter and categorize Events in order to decide on appropriate actions.
- Incident Management
- Process Objective: To manage the lifecycle of all Incidents. The primary objective of Incident Management is to return the IT service to users as quickly as possible.
- Request Fulfilment
- Process Objective: To fulfill Service Requests, which in most cases are minor (standard) Changes (e.g. requests to change a password) or requests for information.
- Access Management
- Process Objective: To grant authorized users the right to use a service, while preventing access to non-authorized users. The Access Management processes essentially execute policies defined in Information Security Management. Access Management is sometimes also referred to as Rights Management or Identity Management.
- Problem Management
- Process Objective: To manage the lifecycle of all Problems. The primary objectives of Problem Management are to prevent Incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. Proactive Problem Management analyzes Incident Records, and uses data collected by other IT Service Management processes to identify trends or significant Problems.
- IT Operations Control
- Process Objective: To monitor and control the IT services and their underlying infrastructure. The process IT Operations Control executes day-to-day routine tasks related to the operation of infrastructure components and applications. This includes job scheduling, backup and restore activities, print and output management, and routine maintenance.
- Facilities Management
- Process Objective: To manage the physical environment where the IT infrastructure is located. Facilities Management includes all aspects of managing the physical environment, for example power and cooling, building access management, and environmental monitoring.
- Application Management
- Process Objective: Application Management is responsible for managing applications throughout their lifecycle.
- Technical Management
- Process Objective: Technical Management provides technical expertise and support for the management of the IT infrastructure.
KPIs | Templates | Roles
- KPIs for Service Operation
- Service Operation templates and checklists
- ITIL roles within Service Operation
Downloads
|
Use the following links to open the process overview of Service Operation showing the most important interfaces: |
 |
Demo Service Operation: ITIL Process Map
The ITIL Process Map video shows samples of the ITIL process templates with contents from Service Operation and Incident Management processes, including the
- high-level view of the ITIL Service Lifecycle (Level 0)
- overview of the Service Operation process (Level 1)
- overview of the Incident Management process (Level 2)
- detailed process flow for the process "Incident Resolution by 1st Level Support" (Level 3)
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Event Management › Incident Mgmt. › Request Fulfilment › Access Mgmt. › Problem Mgmt. › [...]






