Access Management

Objective: Access Management aims to grant authorized users the right to use a service, while preventing access to non-authorized users. This ITIL process essentially executes policies defined in Information Security Management. Access Management is sometimes also referred to as 'Rights Management' or 'Identity Management'.
Part of: Service Operation
Process Owner: Access Manager
Process Description
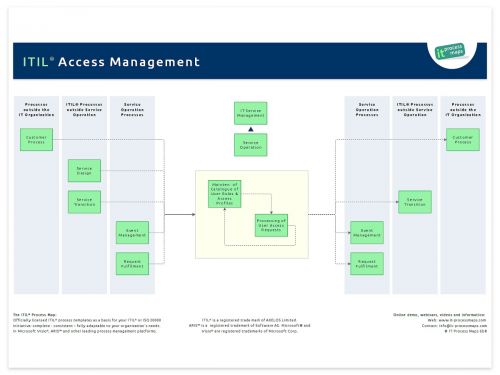
Access Management has been added as a new process to ITIL V3. The decision to include this dedicated process was motivated by Information security reasons, as granting access to IT services and applications only to authorized users is of high importance from an Information Security viewpoint.
In ITIL 2011 an interface between Access Management and Event Management has been added, to emphasize that (some) Event filtering and correlation rules should be designed by Access Management to support the detection of unauthorized access to services. The process overview of ITIL Access Management shows the key information flows (see fig. 1).
A specific activity has been added to revoke access rights if required. And it has been made clearer in the Request Fulfilment and Incident Management processes that the requester's authorization must be checked.
ITIL 4 refers to 'Access Management' as a general management practice - as part of "Information security management".
Sub-Processes
These are the ITIL Access Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
Maintenance of Catalogue of User Roles and Access Profiles
- Process Objective: To make sure that the catalogue of User Roles and Access Profiles is still appropriate for the services offered to customers, and to prevent unwanted accumulation of access rights.
Processing of User Access Requests
- Process Objective: To process requests to add, change or revoke access rights, and to make sure that only authorized users are granted the right to use a service.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in the Access Management process to represent process outputs and inputs:
Access Rights
- A set of data defining what services a user is allowed to access. This definition is achieved by assigning the user, identified by his User Identity, to one or more User Roles.
Request for Access Rights
- A request to grant, change or revoke the right to use a particular service or access certain assets.
User Identity Record
- A set of data with all the details identifying a user or person. It is used to grant rights to that user or person.
User Identity Request
- A request to create, modify or delete a User Identity.
User Role
- A role as part of a catalogue or hierarchy of all the roles (types of users) in the organization. Access rights are based on the roles that individual users have as part of an organization.
User Role Access Profile
- A set of data defining the level of access to a service or group of services for a certain type of user (User Role). User Role Access Profiles help to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of assets by defining what information computer users can utilize, the programs that they can run, and the modifications that they can make.
User Role Requirements
- Requirements from the business side for the catalogue or hierarchy of user roles (types of users) in the organization. Access rights are based on the roles that individual users have as part of an organization.
Roles | Responsibilities
Access Manager - Process Owner
- The Access Manager grants authorized users the right to use a service, while preventing access to non-authorized users.
- The Access Manager essentially executes policies defined in Information Security Management.
1st Level Support
- The responsibility of 1st Level Support is to register and classify received Incidents and to undertake an immediate effort in order to restore a failed IT service as quickly as possible. If no ad-hoc solution can be achieved, 1st Level Support will transfer the Incident to expert technical support groups (2nd Level Support). 1st Level Support also processes Service Requests and keeps users informed about their Incidents' status at agreed intervals.
| ITIL Role / Sub-Process | Access Manager | 1st Level Support |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance of Catalogue of User Roles and Access Profile | A[1]R[2] | |
| Processing of User Access Requests | A | R[3] |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Access Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Access Management.
[3] According to ITIL, it is quite common for the service desk / 1st level support to be delegated responsibility for providing access to simple services.
Process Implementation: Notes
There are a number of different approaches to implementing Access Management. Depending on the size of an organization the methods applied can be rather complex. In this context, ITIL does not provide a detailed explanation of all aspects of Access Management.
Well-defined interfaces between the business and Access Management are vital to achieve high security standards. Typically, responsibilities of both sides are defined in a dedicated Information Security Policy. This policy would, for example, stipulate that HR is to inform Access Management without delay about employees entering or leaving the company.
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Process Description › Sub-Processes › Definitions › Roles






