ITIL Implementation - Process Controlling: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<p> </p> | |||
Once the [[ITIL Implementation - Process Structure|structure of processes]] and [[ITIL Implementation - Process Interfaces|their interfaces]] are clear one should define the approach for ensuring that those processes are running according to expectations (known as “Process Control”). | |||
<p> </p> | |||
==== Objective of this Project Step ==== | |||
* Determination of [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|measurements (KPIs)]] for the processes to be introduced | |||
* Definition of measurement procedures for the KPIs | |||
* Definition of reporting procedures | |||
<p> </p> | |||
==== Description ==== | ==== Description ==== | ||
A coherent strategy for process control not only helps to assess whether the objectives followed with the ITIL introduction are achieved, but also has long-term benefits, in that it delivers the necessary data for a continuous process improvement. | A coherent strategy for process control not only helps to assess whether the objectives followed with the ITIL introduction are achieved, but also has long-term benefits, in that it delivers the necessary data for a continuous process improvement. | ||
How to decide whether a process “runs well” or not? Objective criteria (quality measurements, | How to decide whether a process “runs well” or not? Objective criteria (quality measurements, also known as [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|Key Performance Indicators or KPIs)]] must be determined for this purpose. | ||
also known as [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|Key Performance Indicators or KPIs)]] must be determined for this purpose. | |||
Only then, when it is clear which quality measurements a process must achieve, can its inner details be confidently designed with these goals in mind. | Only then, when it is clear which quality measurements a process must achieve, can its inner details be confidently designed with these goals in mind. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 37: | ||
===== Determine the Process Owners ===== | ===== Determine the Process Owners ===== | ||
Successful management of a process depends on Process Owners who identify themselves closely with their task, and who are sufficiently empowered and equipped with the necessary means. | Successful management of a process depends on [[Roles within ITIL V3#Process Owner|Process Owners]] who identify themselves closely with their task, and who are sufficiently empowered and equipped with the necessary means. | ||
It is therefore important to have the Process Owners (being the ones responsible for running the processes after their implementation) as active participants in the implementation project, so they should be named at an early stage. | It is therefore important to have the Process Owners (being the ones responsible for running the processes after their implementation) as active participants in the implementation project, so they should be named at an early stage. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 43: | ||
In most cases, the selection of Process Owners is rather straightforward (the Problem Manager will, for example, be the owner of the Problem Management process). | In most cases, the selection of Process Owners is rather straightforward (the Problem Manager will, for example, be the owner of the Problem Management process). | ||
===== Define | ===== Define ITIL Metrics and Measurement Procedures ===== | ||
Process Owners use objective quality criteria to assess whether their processes are running | Process Owners use objective quality criteria to assess whether their processes are running "well". This puts them in a position to decide upon the need for process improvements. | ||
The first step when selecting suitable KPIs must always be to decide upon the overall objectives of a process (Example: A high first-resolution rate at the Service Desk). With these objectives in mind, it will be possible to select KPIs which are suitable to measure a successful process execution. | The first step when selecting suitable [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|ITIL KPIs]] must always be to decide upon the overall objectives of a process (Example: A high first-resolution rate at the [[Roles within ITIL V3#1st Level Support|Service Desk]]). With these objectives in mind, it will be possible to select KPIs which are suitable to measure a successful process execution. | ||
[[image:ITIL-KPIs.jpg|frame|right|alt=ITIL KPIs|ITIL Metrics]] | |||
There are also quantitative measures, which are used by the Process Owner to steer the resources within a process (e.g. the number of Incidents received by the Service Desk over the course of time). | There are also quantitative measures, which are used by the Process Owner to steer the resources within a process (e.g. the number of Incidents received by the Service Desk over the course of time). | ||
| Line 45: | Line 56: | ||
This ITIL Wiki contains a choice of [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|suitable KPIs]]. These KPIs were taken from the ITIL recommendations; they have been in some parts supplemented with elements from COBIT. Where necessary, further suggestions for KPIs are available in several books on IT Service Management. | This ITIL Wiki contains a choice of [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|suitable KPIs]]. These KPIs were taken from the ITIL recommendations; they have been in some parts supplemented with elements from COBIT. Where necessary, further suggestions for KPIs are available in several books on IT Service Management. | ||
Process control should not be about setting up as extensive an arsenal of KPIs as possible: Practice has proven that an over-complex structure of measures creates a disproportionate amount of effort, gains little acceptance, and after a short period, is no longer applied.Rather, few significant measures should be defined so that KPI measurement and reporting may be executed with a justifiable amount of time and effort. | Process control should not be about setting up as extensive an arsenal of KPIs as possible: Practice has proven that an over-complex structure of measures creates a disproportionate amount of effort, gains little acceptance, and after a short period, is no longer applied. Rather, few significant measures should be defined so that KPI measurement and reporting may be executed with a justifiable amount of time and effort. | ||
===== Set KPI targets ===== | ===== Set KPI targets ===== | ||
Target values for the KPIs define | Target values for the KPIs define "success" in an objective way and set goals for the Process Owner. It must be noted, however, that target values (like first-time resolution rates) cannot be easily transferred from business to business without precaution. | ||
It is recommendable not to define fixed KPI targets initially, but to merely select suitable KPIs and start measuring. Once a statistically significant number of measurement results are present after a certain time there will be a more solid base for setting targets. | It is recommendable not to define fixed KPI targets initially, but to merely select suitable KPIs and start measuring. Once a statistically significant number of measurement results are present after a certain time there will be a more solid base for setting targets. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 68: | ||
Reporting on process quality is the final element within process control. Reporting procedures must be defined, specifying which KPIs are reported in which form to particular recipients. | Reporting on process quality is the final element within process control. Reporting procedures must be defined, specifying which KPIs are reported in which form to particular recipients. | ||
<p> </p> | |||
==== Prerequisites ==== | ==== Prerequisites ==== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 74: | ||
* [[ITIL Implementation - Process Structure|Structure of the ITIL processes]] to be introduced | * [[ITIL Implementation - Process Structure|Structure of the ITIL processes]] to be introduced | ||
* [[ITIL Processes|Process objectives]] | * [[ITIL Processes|Process objectives]] | ||
<p> </p> | |||
==== Results/ Deliverables ==== | ==== Results/ Deliverables ==== | ||
| Line 73: | Line 82: | ||
* Measurement procedures for the KPIs | * Measurement procedures for the KPIs | ||
* Specification of reporting procedures | * Specification of reporting procedures | ||
<p> </p> | |||
==== Success Factors ==== | ==== Success Factors ==== | ||
* Only KPIs which are actually measurable must be used | * Only KPIs which are actually measurable must be used | ||
* IT Management should make a point of the fact that the use of KPIs serves the purpose of improving processes and not the penalization of employees. There might otherwise be the danger of the participants developing strategies in order to tweak the statistics in their favor, which would be against the interests of the IT organization on the whole. | |||
* Targets for KPIs (especially in the initial phase after the introduction of new processes) are to be reviewed at regular intervals; it is not always necessarily best to strive for top grades – under certain circumstances it is, for example, acceptable to have a lower initial resolution-rate at the Service Desk, if many of the inquiries necessitate specialist knowledge. | |||
<p> </p> | |||
==== <span style="color:#5d5d5d">Relevant Views of the ITIL Process Map V3</span>==== | ==== <span style="color:#5d5d5d">Relevant Views of the ITIL Process Map V3</span>==== | ||
<span style="color:#5d5d5d">The [https://en.it-processmaps.com/products/itil-process-map.html ITIL Process Map V3] contains a choice of suitable KPIs for the most important ITIL processes. Additional suggestions for KPIs are available in the [[Additional Information on ITIL|ITIL core books]] and in several other books on IT Service Management.</span> | <span style="color:#5d5d5d">The [https://en.it-processmaps.com/products/itil-process-map.html ITIL Process Map V3] contains a choice of [[ITIL Key Performance Indicators|suitable KPIs]] for the most important ITIL processes. Additional suggestions for KPIs are available in the [[Additional Information on ITIL|ITIL core books]] and in several other books on IT Service Management.</span> | ||
<p> </p> | |||
'''Following Project Activity''': | '''Following Project Activity''': | ||
| Line 90: | Line 105: | ||
→ ITIL Implementation - Step 8: '''[[ITIL Implementation - Process Design|Designing the Processes in Detail]]''' | → ITIL Implementation - Step 8: '''[[ITIL Implementation - Process Design|Designing the Processes in Detail]]''' | ||
<p> </p> | |||
<!-- This page is assigned to the following categories: --> | <!-- This page is assigned to the following categories: --> | ||
[[Category:ITIL V3]][[Category:ITIL implementation]] | [[Category:ITIL V3]][[Category:ITIL implementation]] | ||
<!-- --- --> | <!-- --- --> | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 16 September 2011
<seo metakeywords="itil process control, itil control, itil procedures and processes" metadescription="A coherent strategy for ITIL process control not only helps to assess whether the objectives followed with the ITIL introduction are achieved, ..." />

| Step 7: Establishing ITIL Process Control |
Once the structure of processes and their interfaces are clear one should define the approach for ensuring that those processes are running according to expectations (known as “Process Control”).
Objective of this Project Step
- Determination of measurements (KPIs) for the processes to be introduced
- Definition of measurement procedures for the KPIs
- Definition of reporting procedures
Description
A coherent strategy for process control not only helps to assess whether the objectives followed with the ITIL introduction are achieved, but also has long-term benefits, in that it delivers the necessary data for a continuous process improvement.
How to decide whether a process “runs well” or not? Objective criteria (quality measurements, also known as Key Performance Indicators or KPIs) must be determined for this purpose.
Only then, when it is clear which quality measurements a process must achieve, can its inner details be confidently designed with these goals in mind.
Determine the Process Owners
Successful management of a process depends on Process Owners who identify themselves closely with their task, and who are sufficiently empowered and equipped with the necessary means.
It is therefore important to have the Process Owners (being the ones responsible for running the processes after their implementation) as active participants in the implementation project, so they should be named at an early stage.
In most cases, the selection of Process Owners is rather straightforward (the Problem Manager will, for example, be the owner of the Problem Management process).
Define ITIL Metrics and Measurement Procedures
Process Owners use objective quality criteria to assess whether their processes are running "well". This puts them in a position to decide upon the need for process improvements.
The first step when selecting suitable ITIL KPIs must always be to decide upon the overall objectives of a process (Example: A high first-resolution rate at the Service Desk). With these objectives in mind, it will be possible to select KPIs which are suitable to measure a successful process execution.
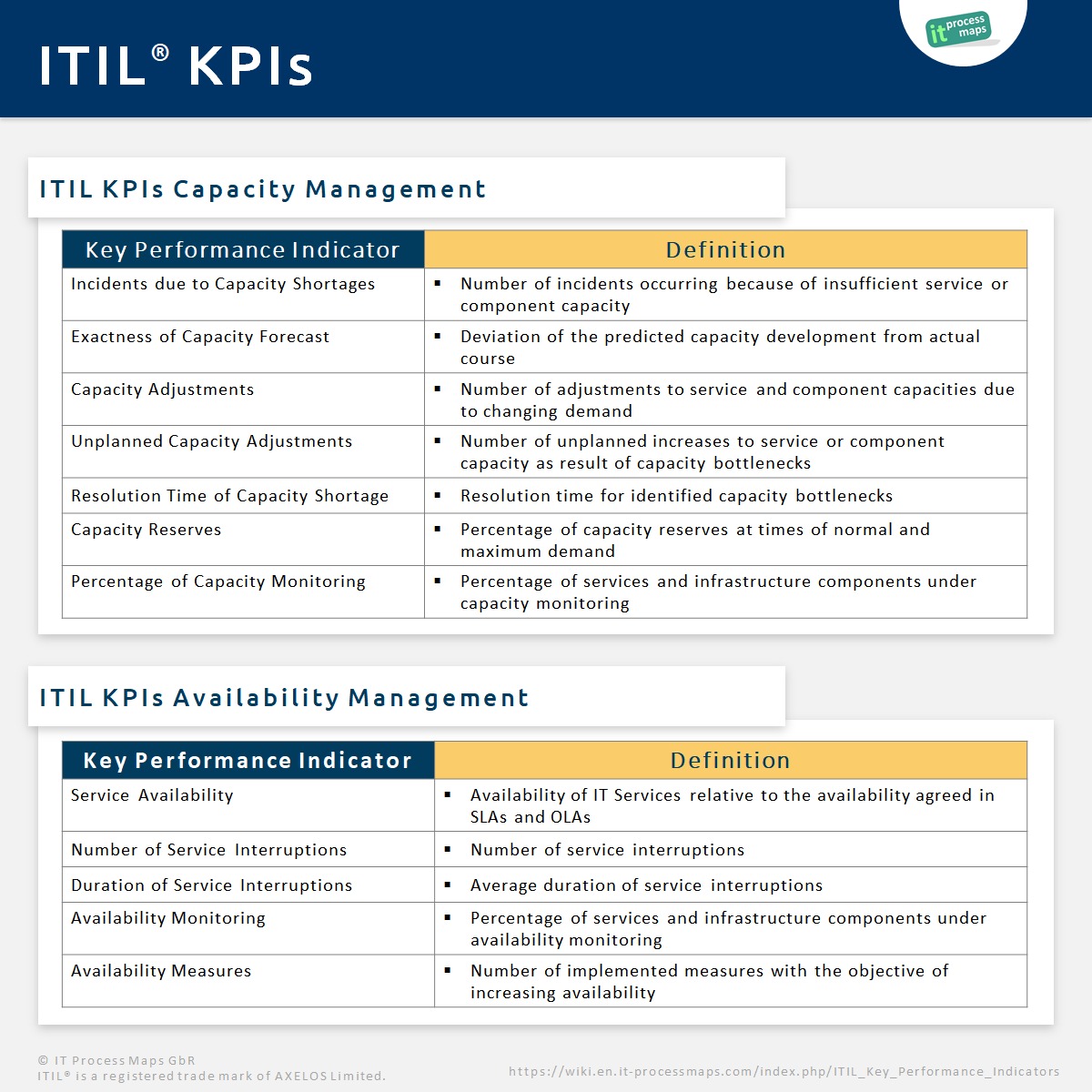
There are also quantitative measures, which are used by the Process Owner to steer the resources within a process (e.g. the number of Incidents received by the Service Desk over the course of time).
Which KPIs are eventually chosen is dependent, amongst other things, upon the available possibilities for their measurement. Ideally, KPIs can be computed automatically, e. g. via a Service Desk system. The measurement procedures defined here are therefore also requirements for the systems to be implemented.
This ITIL Wiki contains a choice of suitable KPIs. These KPIs were taken from the ITIL recommendations; they have been in some parts supplemented with elements from COBIT. Where necessary, further suggestions for KPIs are available in several books on IT Service Management.
Process control should not be about setting up as extensive an arsenal of KPIs as possible: Practice has proven that an over-complex structure of measures creates a disproportionate amount of effort, gains little acceptance, and after a short period, is no longer applied. Rather, few significant measures should be defined so that KPI measurement and reporting may be executed with a justifiable amount of time and effort.
Set KPI targets
Target values for the KPIs define "success" in an objective way and set goals for the Process Owner. It must be noted, however, that target values (like first-time resolution rates) cannot be easily transferred from business to business without precaution.
It is recommendable not to define fixed KPI targets initially, but to merely select suitable KPIs and start measuring. Once a statistically significant number of measurement results are present after a certain time there will be a more solid base for setting targets.
Define the Reporting Procedures
Reporting on process quality is the final element within process control. Reporting procedures must be defined, specifying which KPIs are reported in which form to particular recipients.
Prerequisites
- Structure of the ITIL processes to be introduced
- Process objectives
Results/ Deliverables
- Assignment of Process Owners
- Measurements (KPIs)
- Measurement procedures for the KPIs
- Specification of reporting procedures
Success Factors
- Only KPIs which are actually measurable must be used
- IT Management should make a point of the fact that the use of KPIs serves the purpose of improving processes and not the penalization of employees. There might otherwise be the danger of the participants developing strategies in order to tweak the statistics in their favor, which would be against the interests of the IT organization on the whole.
- Targets for KPIs (especially in the initial phase after the introduction of new processes) are to be reviewed at regular intervals; it is not always necessarily best to strive for top grades – under certain circumstances it is, for example, acceptable to have a lower initial resolution-rate at the Service Desk, if many of the inquiries necessitate specialist knowledge.
Relevant Views of the ITIL Process Map V3
The ITIL Process Map V3 contains a choice of suitable KPIs for the most important ITIL processes. Additional suggestions for KPIs are available in the ITIL core books and in several other books on IT Service Management.
Following Project Activity:
→ ITIL Implementation - Step 8: Designing the Processes in Detail





