Problem Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
</itpmch> | </itpmch> | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-de-es.jpg|DE - ES - Problem Management| | Image:ITIL-Wiki-share.jpg|right|share this page|141px | ||
rect 0 | rect 55 0 99 36 [https://www.linkedin.com/shareArticle?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwiki.en.it-processmaps.com%2Findex.php%2FProblem_Management&hl=en_US&source=IT%20Process%20Wiki share this page on LinkedIn] | ||
rect | rect 97 0 141 36 [https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwiki.en.it-processmaps.com%2Findex.php%2FProblem_Management&text=%23ITILwiki%20%7C%20Problem%20Management%20-%20Process%20description%0A%E2%96%BA&lang=en&via=itprocessmaps share this page on Twitter] | ||
desc none | |||
</imagemap> | |||
<imagemap> | |||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-de-es.jpg|DE - ES - Problem Management|163px | |||
rect 81 0 114 36 [https://wiki.de.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Problem_Management diese Seite auf Deutsch] | |||
rect 115 0 163 36 [https://wiki.es.it-processmaps.com/index.php/ITIL_Gestion_de_Problemas esta página en español] | |||
desc none | desc none | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
<br style="clear:both;"/> | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
'''<span id="Overview">Objective:</span>''' <html><span id="md-webpage-description" itemprop="description"><i>Problem Management</i> aims to manage the lifecycle of all Problems. The primary objectives of this ITIL process are to prevent Incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. 'Proactive Problem Management' analyzes Incident Records, and uses data collected by other IT Service Management processes to identify trends or significant Problems.</span></p> | '''<span id="Overview">Objective:</span>''' <html><span id="md-webpage-description" itemprop="description"><i>Problem Management</i> aims to manage the lifecycle of all Problems. The primary objectives of this ITIL process are to prevent Incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. 'Proactive Problem Management' analyzes Incident Records, and uses data collected by other IT Service Management processes to identify trends or significant Problems.</span></p> | ||
Revision as of 09:34, 28 April 2017


Objective: Problem Management aims to manage the lifecycle of all Problems. The primary objectives of this ITIL process are to prevent Incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. 'Proactive Problem Management' analyzes Incident Records, and uses data collected by other IT Service Management processes to identify trends or significant Problems.
Part of: Service Operation
Process Owner: Problem Manager
Process Description
A new sub-process Major Problem Review was introduced in ITIL V3 to review the solution history of major Problems in order to prevent a recurrence and learn lessons for the future.
In ITIL 2011 the new sub-process Proactive Problem Identification has been added to emphasize the importance of proactive Problem Management.
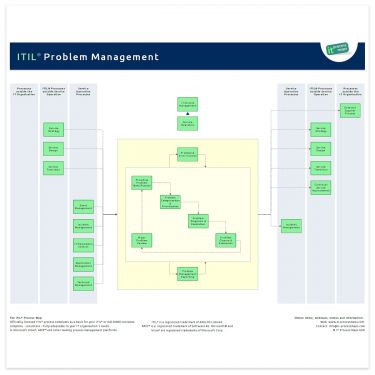
In Problem Categorization and Prioritization, it has been made clearer that categorization and prioritization should be harmonized with the approach used in Incident Management, to facilitate matching between Incidents and Problems. The process overview of ITIL Problem Management is showing the most important interfaces (see Figure 1).
The concept of recreating Problems during Problem Diagnosis and Resolution is now more prominent. This sub-process has been completely revised to provide clearer guidance on how this process cooperates with Incident Management.
Note: The new ITIL 2011 books also contain an expanded section on problem analysis techniques and examples for situations where the various techniques may be applied.
Sub-Processes
These are the ITIL Problem Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
Proactive Problem Identification
- Process Objective: To improve overall availability of services by proactively identifying Problems. Proactive Problem Management aims to identify and solve Problems and/or provide suitable Workarounds before (further) Incidents recur.
Problem Categorization and Prioritization
- Process Objective: To record and prioritize the Problem with appropriate diligence, in order to facilitate a swift and effective resolution.
Problem Diagnosis and Resolution
- Process Objective: To identify the underlying root cause of a Problem and initiate the most appropriate and economical Problem solution. If possible, a temporary Workaround is supplied.
Problem and Error Control
- Process Objective: To constantly monitor outstanding Problems with regards to their processing status, so that where necessary corrective measures may be introduced.
Problem Closure and Evaluation
- Process Objective: To ensure that - after a successful Problem solution - the Problem Record contains a full historical description, and that related Known Error Records are updated.
Major Problem Review
- Process Objective: To review the resolution of a Problem in order to prevent recurrence and learn any lessons for the future. Furthermore it is to be verified whether the Problems marked as closed have actually been eliminated.
Problem Management Reporting
- Process Objective: ITIL Problem Management Reporting aims to ensure that the other Service Management processes as well as IT Management are informed of outstanding Problems, their processing-status and existing Workarounds (see "Problem Management Report").
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in the ITIL Problem Management process to represent process outputs and inputs:
Known Error
- A Known Error is a problem that has a documented root cause and a Workaround. Known Errors are managed throughout their lifecycle by the Problem Management process. The details of each Known Error are recorded in a Known Error Record stored in the Known Error Database (KEDB). As a rule, Known Errors are identified by Problem Management, but Known Errors may also be suggested by other Service Management disciplines, e.g. Incident Management, or by suppliers.
Known Error Database (KEDB)
- The Known Error Database (KEDB) is created by Problem Management and used by Incident and Problem Management to manage all Known Error Records.
Problem
- A cause of one or more Incidents. The cause is not usually known at the time a Problem Record is created.
Problem Management Report
- A report supplying Problem-related information to the other Service Management processes.
Problem Record
- The Problem Record contains all details of a Problem, documenting the history of the Problem from detection to closure (see: ITIL Checklist Problem Record).
Suggested new Known Error
- A suggestion to create a new entry in the Known Error Database, for example raised by the Service Desk or by Release Management. Known Errors are managed throughout their lifecycle by Problem Management.
Suggested new Problem
- A notification about a suspected Problem, handed over to Problem Management for further investigation, possibly leading to the formal logging of a Problem.
Suggested new Workaround
- A suggestion to enter a new Workaround in the Known Error Database, for example raised by the Service Desk or by Release Management. Workarounds are managed throughout their lifecycle by Problem Management.
Workaround
- Workarounds are temporary solutions aimed at reducing or eliminating the impact of Known Errors (and thus Problems) for which a full resolution is not yet available. As such, Workarounds are often applied to reduce the impact of Incidents or Problems if their underlying causes cannot be readily identified or removed.
Templates | KPIs
Roles | Responsibilities
Problem Manager - Process Owner
- The Problem Manager is responsible for managing the lifecycle of all Problems.
- His primary objectives are to prevent Incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of Incidents that cannot be prevented.
- To this purpose he maintains information about Known Errors and Workarounds.
| Responsibility Matrix: ITIL Problem Management | |||
| ITIL Role | Sub-Process | Problem Manager | Applications Analyst[3] | Technical Analyst[3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proactive Problem Identification | A[1]R[2] | - | - |
| Problem Categorization and Prioritization | AR | - | - |
| Problem Diagnosis and Resolution | AR | R | R |
| Problem and Error Control | AR | - | - |
| Problem Closure and Evaluation | AR | - | - |
| Major Problem Review | AR | - | - |
| Problem Management Reporting | AR | - | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Problem Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Problem Management.
[3] see Role descriptions...
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Process Description › Sub-Processes › Definitions › Templates › Roles






