Service Support: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<itpmch><title>Service Support | IT Process Wiki</title> | |||
<meta name="keywords" content="service support, itil service support, itil service support processes" /> | |||
<meta name="description" content="Process Objective: Service Support provides all operative processes necessary for the handling of Service interruptions and for the implementation of Changes; ..." /> | |||
</itpmch> | |||
<imagemap> | |||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-deutsch.jpg|right|ITIL Service Support | |||
default [https://wiki.de.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Service_Support diese Seite auf Deutsch] | |||
desc none | |||
</imagemap> | |||
<br style="clear:both;"/> | |||
'''ITIL Version''': ITIL | '''ITIL Version''': ITIL V2 '''→''' see also ''[[ITIL Processes#ITIL V3 Processes|ITIL V3 2011 Processes]]'' | ||
'''Process Objective''': '''Service Support''' provides all operative Processes necessary for the handling of Service interruptions and for the implementation of Changes; the availability of the IT Services is thereby guaranteed. | '''Process Objective''': '''Service Support''' provides all operative Processes necessary for the handling of Service interruptions and for the implementation of Changes; the availability of the IT Services is thereby guaranteed. | ||
'''Part of:''' [[ITIL Processes#ITIL Processes according to ITIL Version 2 (ITIL V2)|IT Service Management]] | '''Part of:''' [[ITIL Processes#ITIL Processes according to ITIL Version 2 (ITIL V2)|IT Service Management]] | ||
==Sub-Processes of Service Support== | ==Sub-Processes of Service Support== | ||
<imagemap> | |||
Image:overview_service_support_itilv2_thumb.jpg|left|Overview of Service Support, ITIL V2|350px|thumb | |||
default [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/process_overview_service_support_itilv2.pdf ITIL Service Support (.pdf)] | |||
desc bottom-left | |||
</imagemap> | |||
;[[Service Desk and Incident Management]] | ;[[Service Desk and Incident Management]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 28: | ||
;[[Problem Management - ITIL V2|Problem Management]] | ;[[Problem Management - ITIL V2|Problem Management]] | ||
:Process Objective: The objective of Problem Management is to resolve the root cause of Incidents, and to prevent the recurrence of Incidents related to these errors. It provides Incident Management with Temporary Fixes (Workarounds) and Permanent Solutions to Known Errors. Proactive Problem Management identifies and resolves Problems before Incidents occur, for example by | :Process Objective: The objective of Problem Management is to resolve the root cause of Incidents, and to prevent the recurrence of Incidents related to these errors. It provides Incident Management with Temporary Fixes (Workarounds) and Permanent Solutions to Known Errors. Proactive Problem Management identifies and resolves Problems before Incidents occur, for example by analyzing trends in IT Service Usage or by investigating historic Incidents. | ||
;[[Change Management - ITIL V2|Change Management]] | ;[[Change Management - ITIL V2|Change Management]] | ||
:Process Objective: In Change Management, all Changes to the IT infrastructure and its components (Configuration Items) are | :Process Objective: In Change Management, all Changes to the IT infrastructure and its components (Configuration Items) are authorized and documented, in order to ensure that interruptive effects upon the running operation are kept to a minimum. The implementation steps are planned and communicated, in order to recognize potential side-effects as early as possible. The Change Manager and (for further-reaching Changes) the Change Advisory Board (CAB) bear the responsibility for this. A specific procedure is in existence for emergencies, dealing with Urgent Changes. | ||
;[[Release Management|Release Management]] | ;[[Release Management|Release Management]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 37: | ||
;[[Configuration Management|Configuration Management]] | ;[[Configuration Management|Configuration Management]] | ||
Process Objective: The information about Infrastructure and Services necessary for the IT Service Management is made available by Configuration Management. Changes are documented and the updated status of the information is regularly checked. With this, updated and historical information as to the Configuration Items (CIs) are continuously available within the Configuration Management Database (CMDB). | :Process Objective: The information about Infrastructure and Services necessary for the IT Service Management is made available by Configuration Management. Changes are documented and the updated status of the information is regularly checked. With this, updated and historical information as to the Configuration Items (CIs) are continuously available within the Configuration Management Database (CMDB). | ||
==[ Infobox ]== | |||
<html><table class="wikitable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Link to this page:</td> | |||
<td><a itemprop="url" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Service_Support">https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Service_Support</a></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Languages:</td> | |||
<td><span itemprop="inLanguage" content="en">English</span> | <span><a itemprop="citation" class="external text" href="https://wiki.de.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Service_Support">Deutsch</a></span></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Image:</td> | |||
<td style="vertical-align:top"><a itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/f/fa/Overview_service_support_itilv2_thumb.jpg" title="Overwiew of Service Support ITIL V2">Overwiew of Service Support ITIL V2 (.JPG)</a></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Author:</td> | |||
<td><span itemprop="author">Andrea Kempter</span>, <span itemprop="creator copyrightHolder publisher">IT Process Maps</span> <a rel="author" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/andreakempter"><img style="margin:0px 0px 0px 0px;" src="/images/bookmarking/linkedin.png" width="16" height="16" title="By: Andrea Kempter | Profile on LinkedIn" alt="Author: Andrea Kempter, IT Process Maps GbR" /></a></td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table></html> | |||
<p> </p> | |||
<!-- This page is assigned to the following categories: --> | |||
[[Category:ITIL V2|!]][[Category:ITIL discipline]][[Category:ITIL process]][[Category:Service Support|!]] | |||
<!-- --- --> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 30 March 2019

ITIL Version: ITIL V2 → see also ITIL V3 2011 Processes
Process Objective: Service Support provides all operative Processes necessary for the handling of Service interruptions and for the implementation of Changes; the availability of the IT Services is thereby guaranteed.
Part of: IT Service Management
Sub-Processes of Service Support
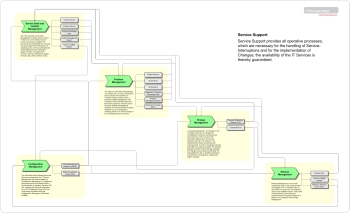
- Service Desk and Incident Management
- Process Objective: The "Service Desk and Incident Management" process aims to restore IT Services to their defined Service Levels as quickly as possible The process is also responsible for receiving and processing Service Requests, for assisting users, and for coordinating the Incident Resolution with Specialist Support Groups. Throughout the process, users are informed at regular intervals about their Incidents' status.
- Problem Management
- Process Objective: The objective of Problem Management is to resolve the root cause of Incidents, and to prevent the recurrence of Incidents related to these errors. It provides Incident Management with Temporary Fixes (Workarounds) and Permanent Solutions to Known Errors. Proactive Problem Management identifies and resolves Problems before Incidents occur, for example by analyzing trends in IT Service Usage or by investigating historic Incidents.
- Change Management
- Process Objective: In Change Management, all Changes to the IT infrastructure and its components (Configuration Items) are authorized and documented, in order to ensure that interruptive effects upon the running operation are kept to a minimum. The implementation steps are planned and communicated, in order to recognize potential side-effects as early as possible. The Change Manager and (for further-reaching Changes) the Change Advisory Board (CAB) bear the responsibility for this. A specific procedure is in existence for emergencies, dealing with Urgent Changes.
- Release Management
- Process Objective: Release Management is the central responsible body for the implementation of Changes to the IT Infrastructure, so that these are carried out in an effective, secure and verifiable manner. Their tasks include planning, monitoring and implementation of respective Rollouts or Rollins in co-ordination with Change Management.
- Configuration Management
- Process Objective: The information about Infrastructure and Services necessary for the IT Service Management is made available by Configuration Management. Changes are documented and the updated status of the information is regularly checked. With this, updated and historical information as to the Configuration Items (CIs) are continuously available within the Configuration Management Database (CMDB).
[ Infobox ]
| Link to this page: | https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Service_Support |
| Languages: | English | Deutsch |
| Image: | Overwiew of Service Support ITIL V2 (.JPG) |
| Author: | Andrea Kempter, IT Process Maps |






