ITIL Processes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | <meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | ||
<meta property="og:image:height" content="900" /> | <meta property="og:image:height" content="900" /> | ||
<link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | <link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | ||
</itpmch> | </itpmch> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:46, 31 December 2023

Objective: IT service providers implement ITIL processes to ensure their services are delivered in a customer-focused, quality-driven and economical way.
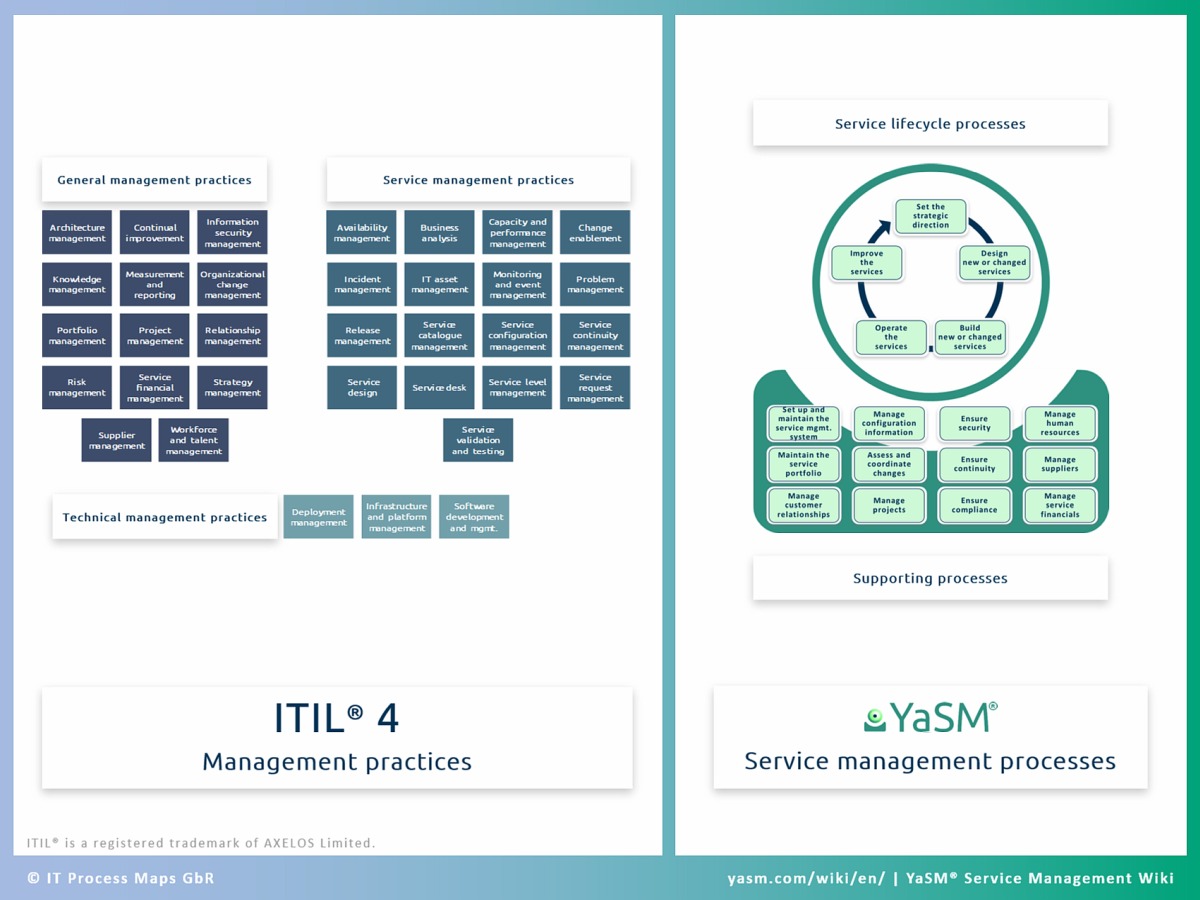
ITIL 4 Processes
While earlier versions of ITIL defined specific sets of processes, ITIL 4 describes 34 'practices'. This gives organizations more freedom to design tailor-made ITIL processes, in line with their specific requirements.
The 5 ITIL stages and 26 ITIL V3 processes have not been invalidated with the publication of ITIL 4 and they are still widely used [1].
But the arrival of ITIL 4, with its strong preference for reduced complexity and 'simple and practical solutions', provides an opportunity for a fresh start with leaner ITIL processes that are easier to use.
We describe such a leaner set of 19 service management processes in the YaSM Wiki.
ITIL Processes according to ITIL V3
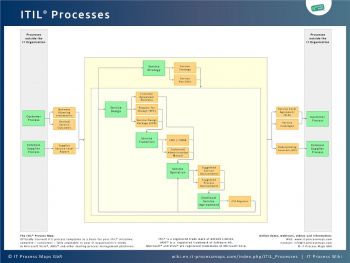
ITIL V3 (ITIL 2011) organizes the ITIL processes around the five service lifecycle stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (see fig. 2). Each of the five stages is focused on a specific phase of the service lifecycle:
- Service Strategy
- Process Objective: To decide on a strategy to serve customers. Starting from an assessment of customer needs and the market place, the Service Strategy process determines which services the IT organization is to offer and what capabilities need to be developed. Its ultimate goal is to make the IT organization think and act in a strategic manner.
- Service Design
- Process Objective: To design new IT services. The scope of the process includes the design of new services, as well as changes and improvements to existing ones.
- Service Transition
- Process Objective: To build and deploy IT services. Service Transition also makes sure that changes to services and Service Management processes are carried out in a coordinated way.
- Service Operation
- Process Objective: To make sure that IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently. The Service Operation process includes fulfilling user requests, resolving service failures, fixing problems, as well as carrying out routine operational tasks.
- Continual Service Improvement - CSI
- Process Objective: To use methods from quality management in order to learn from past successes and failures. The Continual Service Improvement process aims to continually improve the effectiveness and efficiency of IT processes and services, in line with the concept of continual improvement adopted in ISO 20000.
ITIL Processes according to ITIL Version 2 (ITIL V2)
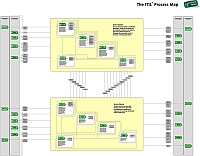
Unlike ITIL V3, IT Service Management according to ITIL version 2 was not organized around the service lifecycle. ITIL V2 included two "disciplines":
- Service Support
- The ITIL discipline Service Support provides all operative Processes necessary for the handling of Service interruptions and for the implementation of Changes; the availability of the IT Services is thereby guaranteed.
- Service Delivery
- The ITIL discipline Service Delivery ensures that binding rules for the operative Processes are in existence. It regulates the planning, contractual and financial topics.
Video and notes
[1] Video: ITIL 4 Process Map - How service providers define ITIL processes that are in tune with ITIL 4.
Is based on: ITIL reference processes from the ITIL Process Map
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Service Strategy › Service Design › Service Transition › Service Operation › Continual Service Improvement