ITIL Implementation - IT Service Structure: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | <meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | ||
<meta property="og:image:height" content="600" /> | <meta property="og:image:height" content="600" /> | ||
<link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | <link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | ||
</itpmch> | </itpmch> | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-de-es.jpg|right|DE - ES - ITIL IT Service Structure|163px | |||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-de-es.jpg|DE - ES - ITIL IT Service Structure|163px | |||
rect 81 0 114 36 [https://wiki.de.it-processmaps.com/index.php/ITIL-Implementierung_-_IT-Services diese Seite auf Deutsch] | rect 81 0 114 36 [https://wiki.de.it-processmaps.com/index.php/ITIL-Implementierung_-_IT-Services diese Seite auf Deutsch] | ||
rect 115 0 163 36 [https://wiki.es.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Implementaci%C3%B3n_de_ITIL_-_Estructura_de_servicios esta página en español] | rect 115 0 163 36 [https://wiki.es.it-processmaps.com/index.php/Implementaci%C3%B3n_de_ITIL_-_Estructura_de_servicios esta página en español] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 31: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
Any ITIL initiative should start by [[#Customer_services_and_supporting_services|looking at services]]. After all, the whole idea behind introducing ITIL is to achieve a better focus on services. | Any ITIL initiative should start by [[#Customer_services_and_supporting_services|looking at services]]. After all, the whole idea behind introducing ITIL best practices is to achieve a better focus on services. | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 52: | ||
In other words, what the customers want is reliable internet access, not a specific sort of network infrastructure (in fact it is irrelevant to the clients that some infrastructure is needed to provide them with internet access). | In other words, what the customers want is reliable internet access, not a specific sort of network infrastructure (in fact it is irrelevant to the clients that some infrastructure is needed to provide them with internet access). | ||
====Creating a list of customer services==== | ====Creating a list of customer services==== | ||
| Line 71: | Line 57: | ||
[[Image:thumb_IT_Services.jpg|thumb|200px|right|none|alt=IT Service Structure|link=https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/File:Thumb_IT_Services.jpg|Fig. 1: [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/service_structure.pdf IT Service Structure - Example (.PDF)]]] | [[Image:thumb_IT_Services.jpg|thumb|200px|right|none|alt=IT Service Structure|link=https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/index.php/File:Thumb_IT_Services.jpg|Fig. 1: [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/service_structure.pdf IT Service Structure - Example (.PDF)]]] | ||
A good way to get started is creating a list of existing customer services, using - if possible - existing agreements and other documentation. If no service-related information is available, a basic list must be drawn from scratch, including at least short service descriptions and an overview of which customers use which services. | A good way to get started is creating a list of existing customer services, using - if possible - existing agreements and other documentation. If no service-related information is available, a basic list must be drawn from scratch, including at least short service descriptions and an overview of which customers use which services. | ||
====Identifying supporting services==== | ====Identifying supporting services==== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 65: | ||
Supporting services are often closely related to certain parts of the technical infrastructure, such as major application systems or infrastructure components: "Providing the SAP environment" would be a typical example. | Supporting services are often closely related to certain parts of the technical infrastructure, such as major application systems or infrastructure components: "Providing the SAP environment" would be a typical example. | ||
====Drawing up the service structure==== | ====Drawing up the service structure==== | ||
Having identified customer and supporting services, the remaining task is to draw up the service structure by determining their interdependencies (see | Having identified customer and supporting services, the remaining task is to draw up the service structure by determining their interdependencies (see fig. 1: [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/service_structure.pdf IT service structure - example (.pdf)]). | ||
Supporting services may be arranged in several layers; for example, a service responsible for operating a certain application system may rely on another supporting service providing a basic operation system environment. | Supporting services may be arranged in several layers; for example, a service responsible for operating a certain application system may rely on another supporting service providing a basic operation system environment. | ||
The service structure drawn up in this project step will be a valuable input at a later point in time, when the [[Service Catalogue Management#Service Catalogue|Service Catalogue Management]] process is being implemented. | The service structure drawn up in this project step will be a valuable input at a later point in time, when the [[Service Catalogue Management#Service Catalogue|Service Catalogue Management]] process is being implemented. | ||
==Prerequisites== | ==Prerequisites== | ||
| Line 95: | Line 78: | ||
* Existing agreements and information | * Existing agreements and information | ||
* Partners on the client-side for the definition of customer services | * Partners on the client-side for the definition of customer services | ||
==Results/ Deliverables== | ==Results/ Deliverables== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 84: | ||
* List of supporting services, including at least short service descriptions, responsible service owners and indications of whether the services are operated with internal or external resources | * List of supporting services, including at least short service descriptions, responsible service owners and indications of whether the services are operated with internal or external resources | ||
* Service structure, describing the service interdependencies. | * Service structure, describing the service interdependencies. | ||
==Success factors== | ==Success factors== | ||
| Line 115: | Line 96: | ||
** Etc. | ** Etc. | ||
*The IT service structure should be created in close coordination with the IT organization's clients. | *The IT service structure should be created in close coordination with the IT organization's clients. | ||
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
[1] IT Process Wiki: [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/service_structure.pdf IT service structure - Template (.pdf)] | [1] IT Process Wiki: [https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/service_structure.pdf IT service structure - Template (.pdf)] | ||
==Following project activity== | ==Following project activity== | ||
→ ITIL Implementation - step 3: '''[[ITIL Implementation - ITIL Roles|Selection of ITIL roles and role owners]]''' | → ITIL Implementation - step 3: '''[[ITIL Implementation - ITIL Roles|Selection of ITIL roles and role owners]]''' | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<html>By:  Andrea Kempter <a rel="author" href="https:// | <html>By:  Andrea Kempter <a rel="author" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/andreakempter"><img style="margin:0px 0px 0px 0px;" src="/images/bookmarking/linkedin.png" width="16" height="16" title="By: Andrea Kempter | Profile on LinkedIn" alt="Author: Andrea Kempter, IT Process Maps GbR" /></a>, IT Process Maps. | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 167: | Line 144: | ||
<meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="Step 2: Definition of the IT Service Structure" /> | <meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="Step 2: Definition of the IT Service Structure" /> | ||
<link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/0/05/Thumb_IT_Services.jpg" /> | <link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/0/05/Thumb_IT_Services.jpg" /> | ||
<link itemprop="author" href="https:// | <link itemprop="author" href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/andreakempter" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="author" content="Andrea Kempter" /> | <meta itemprop="author" content="Andrea Kempter" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="creator copyrightHolder publisher" content="IT Process Maps" /> | <meta itemprop="creator copyrightHolder publisher" content="IT Process Maps" /> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 5 April 2022

| Step 2: Definition of the IT Service Structure |
Any ITIL initiative should start by looking at services. After all, the whole idea behind introducing ITIL best practices is to achieve a better focus on services.
Objectives
- Identification of customer services and supporting services
- Drawing up the service structure by determining the interdependencies between customer services and supporting services
Description
Customer services and supporting services
To get a clear picture of the service provider's range of services, it is advisable to develop a service structure, comprising both customer services and supporting services. This reflects one of the most important principles in ITIL and other service management frameworks: Customer services (services offered to customers) are typically based on a set of supporting services (services visible only inside the service provider organization). Supporting services may be operated with the service provider's own resources or by an external party.
There is often confusion about what exactly is considered a customer service:
- Customer services are characterized by providing value to clients, an example would be a service which allows the clients to send and receive emails and to access the internet.
- Supporting services, in contrast, are not of direct value to clients but are needed as building blocks for customer services. The provision of a suitable network infrastructure, for example, would be a typical supporting service which is required to offer clients an internet access service.
In other words, what the customers want is reliable internet access, not a specific sort of network infrastructure (in fact it is irrelevant to the clients that some infrastructure is needed to provide them with internet access).
Creating a list of customer services
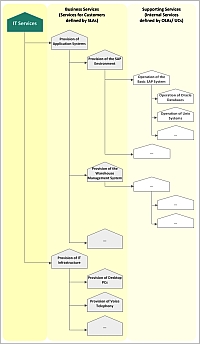
A good way to get started is creating a list of existing customer services, using - if possible - existing agreements and other documentation. If no service-related information is available, a basic list must be drawn from scratch, including at least short service descriptions and an overview of which customers use which services.
Identifying supporting services
One it is clear which business services are provided for the customers it becomes possible to identify the required supporting services.
A key objective of defining supporting services is to assign responsibilities for the delivery of those services: The service owners are responsible for delivering the services in accordance with the agreed service quality levels.
Supporting services are often closely related to certain parts of the technical infrastructure, such as major application systems or infrastructure components: "Providing the SAP environment" would be a typical example.
Drawing up the service structure
Having identified customer and supporting services, the remaining task is to draw up the service structure by determining their interdependencies (see fig. 1: IT service structure - example (.pdf)).
Supporting services may be arranged in several layers; for example, a service responsible for operating a certain application system may rely on another supporting service providing a basic operation system environment.
The service structure drawn up in this project step will be a valuable input at a later point in time, when the Service Catalogue Management process is being implemented.
Prerequisites
- Existing agreements and information
- Partners on the client-side for the definition of customer services
Results/ Deliverables
- List of customer services, including at least short service descriptions and an overview of which customers are using which services
- List of supporting services, including at least short service descriptions, responsible service owners and indications of whether the services are operated with internal or external resources
- Service structure, describing the service interdependencies.
Success factors
- It is not recommended at this stage to ask customers to sign Service Level Agreements: SLAs should be signed at a later point in time, when the services have been formally set up.
- To keep the number of services (and service agreements) manageable, several related service components are often bundled into customer services: A typical customer service offered by IT service providers, "Provision of desktop PCs", may thus include
- Initial installation
- Troubleshooting
- User assistance
- Software updates
- Hardware updates
- Etc.
- The IT service structure should be created in close coordination with the IT organization's clients.
Resources
[1] IT Process Wiki: IT service structure - Template (.pdf)
Following project activity
→ ITIL Implementation - step 3: Selection of ITIL roles and role owners
Notes
By: Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Objectives › Description › Prerequisites › Results/ Deliverables › Success factors






