ITIL Implementation - ITIL Roles


| Step 3: Selection of ITIL Roles and Role Owners |
At the beginning of any ITIL or ISO 20000 initiative it is important to nominate the individuals who will be in charge of running the new ITIL processes. It must be determined what ITIL roles are necessary and to whom those roles are assigned.
Objectives
- Identification of the required ITIL roles, depending on the scope of ITIL processes to be introduced
- Assignment of owners to the roles
Description
To deal with this question at an early stage is of vital importance for the success of the ITIL project: the person who will later have the responsibility for running a certain process should also participate in its design. This will ensure that as much experience as possible flows into the process definition, and that the role owners identify themselves closely with any changes to existing working practices.

The identification of the required ITIL roles (see fig. 1: Index of ITIL roles (.pdf)) is derived directly from the ITIL processes that are to be introduced. If for example Problem Management is in line for introduction, a Problem Manager must be appointed.
Within larger businesses and where considered necessary, the determination of required ITIL roles is not quite as straightforward - a sub-division of the tasks can be necessary, which results in a subdivision of the roles. If the Problem Manager for instance is not able to cope with all the tasks within Problem Management, the introduction of specialist roles such as "Problem Analyst", "Error Manager" etc. must be considered.
At this project stage it is not absolutely necessary to define the ITIL roles in detail, for instance in the form of extensive documents. This will be done implicitly during the subsequent project phases: when processes are defined in detail, single activities are shown together with the roles responsible for their execution.

Based on this information, a RACI matrix is often created to provide a summary of the roles' responsibilities in the processes - some process management systems support the generation of such a matrix (watch the video by IT Process Maps or see fig. 3: ITIL RACI matrix).
Prerequisites
- Identification of the ITIL processes or disciplines which are to be introduced or revised during the project (at least a first guess, as a subsequent as-is assessment might lead to further insights on how to define the project scope)
Results/ Deliverables
- List of the required ITIL roles
- Assignment of owners to the roles
Success factors
At this point, it is crucial to name specific persons as role owners, so that they (as the ones responsible for running the processes in future) are able to contribute the process design in the course of the project. In cases of doubt, it is possible to start out with the obvious ITIL roles, and to later differentiate into sub-roles if necessary.
Relevant views of the ITIL Process Map
The ITIL Process Map includes a list of all the ITIL standard roles complete with their descriptions (see fig. 1: Index of ITIL roles). The roles required for the project may be chosen from this inventory.
The ITIL roles are used in the process diagrams to illustrate the responsibilities for performing single activities.
ITIL RACI matrix
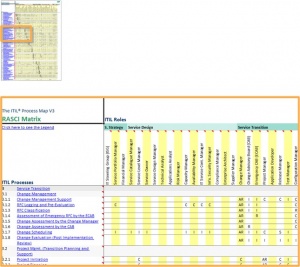
The ITIL roles also figure in the top row of the RASCI matrix that comes with the ITIL Process Map (see fig. 3):
The RASCI matrix and the process diagrams are designed to be used in combination. The matrix provides a summary of the roles’ responsibilities in all processes, while the diagrams show in detail which roles are responsible for performing certain activities within a process.
The RASCI matrix may also be used for assigning owners to the various roles, or this can be done in the organization charts.
Resources
- [1] Index of ITIL roles (.pdf)
- [2] ITIL role definitions
- [3] Detailed responsibility matrices for all ITIL processes and sub-processes here in our Wiki, f.i. roles and responsibilities in Incident Management
- [4] More on responsibility matrices, following the RACI model; IT Process Maps.
Following project activity
→ ITIL Implementation - Step 4: Analysis of As-Is Processes: ITIL-Assessment
Notes
By: Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Objectives › Description › Prerequisites › Results/ Deliverables › Success factors






