Event Management

Objective: The objective of ITIL Event Management is to make sure CIs and services are constantly monitored. ''Event Management'' aims to filter and categorize Events in order to decide on appropriate actions if required.
Part of: Service Operation
Process Owner: IT Operations Manager
Process Description
Essentially, the activities and process objectives of the Event Management process are identical in ITIL V3 and V2 (Event Management was part of ICT Infrastructure Management).
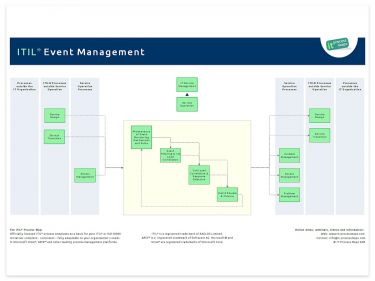
Interfaces between Event Management and the other ITIL processes were adjusted in order to reflect the new ITIL process structure in ITIL V3.
In ITIL 2011 Event Management has been updated to reflect the concept of 1st Level Correlation and 2nd Level Correlation.
The process flows (see Fig. 1) reflect the more detailed guidance in the ITIL 2011 books. The process overview of ITIL Event Management is showing the most important interfaces (see Figure 1).
Sub-Processes
These are the ITIL Event Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
Maintenance of Event Monitoring Mechanisms and Rules
- Process Objective: To set up and maintain the mechanisms for generating meaningful Events and effective rules for their filtering and correlating.
Event Filtering and 1st Level Correlation
- Process Objective: To filter out Events which are merely informational and can be ignored, and to communicate any Warning and Exception Events.
2nd Level Correlation and Response Selection
- Process Objective: To interpret the meaning of an Event and select a suitable response if required.
Event Review and Closure
- Process Objective: To check if Events have been handled appropriately and may be closed. This process also makes sure that Event logs are analyzed in order to identify trends or patterns which suggest corrective action must be taken.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in the ITIL Event Management process to represent process outputs and inputs:
Event
- see Event Record
Event Categorization Scheme
- The Categorization Scheme for Events supports a consistent approach to dealing with specific types of Events. Ideally, this scheme should be harmonized with the schemes to categorize CIs, Incidents and Problems.
Event Filtering and Correlation Rules
- Rules and criteria used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring systems. Some of those rules are defined during the Service Design stage, for example to ensure that Events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered.
Event Record
- A record describing a change of state which has significance for the management of a Configuration Item or service. The term Event is also used to mean an alert or notification created by any IT service, Configuration Item or monitoring tool. Events often require IT operations personnel to take actions, and may lead to Incidents being logged.
Event Trends and Patterns
- Any trends and patterns identified during analysis of significant Events, which suggest that improvements to the infrastructure are needed.
Roles | Responsibilities
IT Operations Manager - Process Owner
- An IT Operations Manager will be needed to take overall responsibility for a number of Service Operation activities. For instance, this role will ensure that all day-to-day operational activities are carried out in a timely and reliable way.
IT Operator
- IT Operators are the staff who perform the day-to-day operational activities.
- Typical responsibilities include: Performing backups, ensuring that scheduled jobs are performed, installing standard equipment in the data center.
| Responsibility Matrix: ITIL Event Management | ||||
| ITIL Role / Sub-Process | IT Operations Manager | IT Operator | (Event Monitoring System) | Other roles involved [3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maintenance of Event Monitoring Mechanisms and Rules | A[1]R[2] | R | - | R |
| Event Filtering and 1st Level Correlation | A | - | R | - |
| 2nd Level Correlation and Response Selection | A | R | R | - |
| Event Review and Closure | AR | - | - | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Event Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Event Management.
[3] In cooperation, as appropriate: IT Operations Manager, Access Manager, Capacity Manager, Availability Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, Information Security Manager, Applications Analyst and/ or technical Analyst. → Role descriptions...
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Process Description › Sub-Processes › Definitions › Roles






