Risk Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | <meta property="og:image:width" content="1200" /> | ||
<meta property="og:image:height" content="1200" /> | <meta property="og:image:height" content="1200" /> | ||
<link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | <link href="https://plus.google.com/108613479011811316823/posts" rel="publisher" /> | ||
</itpmch> | </itpmch> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:52, 31 December 2023

Objective: The objective of ITIL Risk Management is to identify, assess and control risks. This includes analyzing the value of assets to the business, identifying threats to those assets, and evaluating how vulnerable each asset is to those threats.
Part of: Service Design
Process Owner: Risk Manager
Process Description
Risk management is not on the list of official ITIL 2011 processes, but concepts for dealing with risks are described in several ITIL processes, and ITIL calls for "coordinated risk assessment exercises". So there are good reasons for organizations to define and implement a risk management process, and at IT Process Maps we decided to introduce a specific Risk Management process as part of the ITIL® Process Map.
Having a basic Risk Management process in place will provide a good starting point for introducing best-practice Risk Management frameworks like M_o_R (as recommended in the ITIL V3 books).
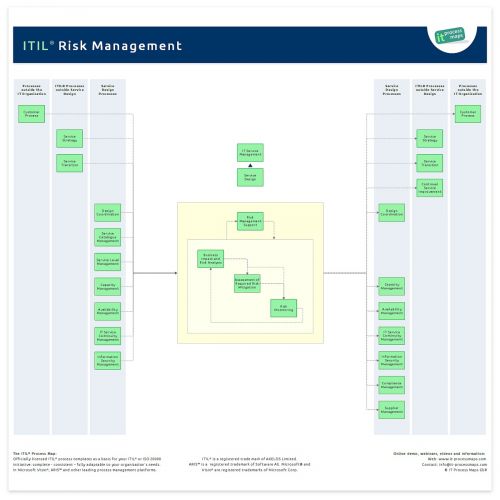
Following the introduction of Design Coordination in ITIL 2011 the information flows have been adapted slightly. The process overview of ITIL Risk Management (.JPG) shows the key information flows (see fig. 1).
ITIL 4 refers to 'Risk Management' as a general management practice.
Sub-Processes
These are the ITIL Risk Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
Risk Management Support
- Process Objective: To define a framework for Risk Management. Most importantly, this process specifies how risk is quantified, what risks the organization is willing to accept, and who is in charge of the various Risk Management duties.
Business Impact and Risk Analysis
- Process Objective: To quantify the impact to the business that a loss of service or asset would have, and to determine the likelihood of a threat or vulnerability to actually occur. The result of the "Business Impact and Risk Analysis" is the Risk Register, a prioritized list of risks which must be subsequently addressed.
Assessment of Required Risk Mitigation
- Process Objective: To determine where risk mitigation measures are required, and to identify Risk Owners who will be responsible for their implementation and ongoing maintenance.
Risk Monitoring
- Process Objective: To monitor the progress of counter measure implementation, and to take corrective action where necessary.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in the ITIL Risk Management process to represent process outputs and inputs:
Business Impact and Risk Analysis
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and Risk Analysis are concepts associated with Risk Management. Their ultimate goal is to identify which risks must be managed and addressed by risk mitigation measures.
Process and Asset Valuation
- An estimate of the value a process or other asset represents for the business. This value is an important input for Risk Analysis.
Risk Management Policy
- The Risk Management Policy describes and communicates the organization’s approach to managing risk. Most importantly, it defines how risk is quantified and who is in charge of specific risk management duties. The Risk Management Policy is maintained by the Risk Manager role, but to be effective it needs the backing of senior management.
Risk Register
- The Risk Register is a tool used by the Risk Management process to keep an overview of identified risks and corresponding counter measures. The Risk Register is sometimes referred to as the Risk Log.
Roles | Responsibilities
Risk Manager - Process Owner
- The Risk Manager is responsible for identifying, assessing and controlling risks. This includes analyzing the value of assets to the business, identifying threats to those assets, and evaluating how vulnerable each asset is to those threats.
| ITIL Role / Sub-Process | Risk Manager | Other roles involved |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management Support | A[1]R[2] | - |
| Business Impact and Risk Analysis | AR | R[3] |
| Assessment of Required Risk Mitigation | AR | - |
| Risk Monitoring | AR | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the ITIL Risk Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Risk Management.
[3] Availability Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, Information Security Manager, Compliance Manager, and Supplier Manager (see → Role descriptions)
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
Process Description › Sub-Processes › Definitions › Roles






