Service Level Management: Difference between revisions
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Process Description == | == Process Description == | ||
Service Level Management has been completely redesigned in '''''ITIL 2011''''' following the introduction of the [[ITIL Design Coordination|Design Coordination]] process. | |||
[[Image:Service-level-management.jpg|right|thumb|375px|alt=Service Level Management ITIL|[https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/process_overview_service_level_management_itilv3.pdf Service Level Management]]] | [[Image:Service-level-management.jpg|right|thumb|375px|alt=Service Level Management ITIL|[https://wiki.en.it-processmaps.com/images/pdf/process_overview_service_level_management_itilv3.pdf Service Level Management]]] | ||
Coordinating activities have been removed. | |||
Service Level Management is now mainly responsible for [[#Service Level Management Requirements|gathering service requirements]], as well as [[#ITIL Service Level Management Reporting|monitoring and reporting]] with regards to [[#Service Level Management Agreements|agreed service levels]]. | Service Level Management is now mainly responsible for [[#Service Level Management Requirements|gathering service requirements]], as well as [[#ITIL Service Level Management Reporting|monitoring and reporting]] with regards to [[#Service Level Management Agreements|agreed service levels]]. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
== Definitions == | == Definitions == | ||
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (''information objects'') are used in ITIL Service Level Management to represent process outputs and inputs: | The following [[ITIL Glossary#ITIL Glossary A-Z|ITIL terms and acronyms]] (''information objects'') are used in ITIL Service Level Management to represent process outputs and inputs: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 63: | ||
;<span id="OLA">Operational Level Agreement (OLA)</span> | ;<span id="OLA">Operational Level Agreement (OLA)</span> | ||
:An agreement between an IT service provider and another part of the same organization. An OLA supports the IT service provider's delivery of services to customers. The OLA defines the goods or services to be provided and the responsibilities of both parties. For example there could be an OLA - between the IT service provider and a procurement department to obtain hardware in agreed times - between the Service Desk and a support group to provide Incident resolution in agreed times (see also: [[Checklist SLA OLA | :An agreement between an IT service provider and another part of the same organization. An OLA supports the IT service provider's delivery of services to customers. The OLA defines the goods or services to be provided and the responsibilities of both parties. For example there could be an OLA - between the IT service provider and a procurement department to obtain hardware in agreed times - between the Service Desk and a support group to provide Incident resolution in agreed times (see also: [[Checklist SLA OLA|ITIL Checklist SLA - OLA]]). | ||
;Outline of Service Requirements | ;<span id="Service Requirements">Outline of Service Requirements</span> | ||
:The desired outcome of a service, stated in terms of required service functionality | :The desired outcome of a service, stated in terms of required service functionality (utility) and service levels (warranty). Based on this information, detailed service requirements are specified during the Service Design stage. | ||
;<span id="SAC">Service Acceptance Criteria (SAC)</span> | ;<span id="SAC">Service Acceptance Criteria (SAC)</span> | ||
:A set of criteria used to ensure that an IT service meets its functionality and quality requirements and that the service provider is ready to operate the new service when it has been deployed. | :A set of criteria used for service acceptance testing to ensure that an IT service meets its functionality and quality requirements and that the service provider is ready to operate the new service when it has been deployed. | ||
;<span id="SLA">Service Level Agreement (SLA)</span> | ;<span id="SLA">Service Level Agreement (SLA)</span> | ||
:An agreement between an IT service provider and a customer. The SLA describes the IT service, documents service level targets, and specifies the responsibilities of the IT service provider and the customer. A single SLA may cover multiple services or multiple customers (see also: [[Checklist SLA OLA | :An agreement between an IT service provider and a customer. The SLA describes the IT service, documents service level targets, and specifies the responsibilities of the IT service provider and the customer. A single SLA may cover multiple services or multiple customers (see also: [[Checklist SLA OLA|ITIL Checklist SLA - OLA]]). | ||
;<span id="Service Level Report">Service Level Report</span> | ;<span id="Service Level Report">Service Level Report</span> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 78: | ||
;<span id="SLR">Service Level Requirements (SLR)</span> | ;<span id="SLR">Service Level Requirements (SLR)</span> | ||
:The Service Level Requirements document contains the requirements for a service from the client viewpoint, defining detailed service level targets, mutual responsibilities, and other requirements specific to a certain (group of) customers. | :The Service Level Requirements document contains the requirements for a service from the client viewpoint, defining detailed service level targets, mutual responsibilities, and other requirements specific to a certain (group of) customers. As the service enters new stages of its life cycle, the SLR document evolves into a draft [[Service Level Management#SLA|Service Level Agreement]]. | ||
;<span id="SLM Document Templates">SLM Document Templates</span> | ;<span id="SLM Document Templates">SLM Document Templates</span> | ||
| Line 92: | Line 88: | ||
* [[ITIL KPIs Service Design#ITIL KPIs Service Level Management|Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Service Level Management]] | * [[ITIL KPIs Service Design#ITIL KPIs Service Level Management|Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Service Level Management]] | ||
* [[ITIL-Checklists# | * [[ITIL-Checklists#Service Level Management|Checklists Service Level Management]]: | ||
** [[Checklist SLA OLA | ** [[Checklist SLA OLA|Checklist Service Level Agreement (SLA) - Operational Level Agreement (OLA)]], and | ||
** [[Checklist Service Level Requirements (SLR)]] | ** [[Checklist Service Level Requirements (SLR)]] | ||
** [[Checklist Service Level Report]] | ** [[Checklist Service Level Report]] | ||
| Line 112: | Line 108: | ||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" style="text-align:center;" valign="top" | {| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" style="text-align:center;" valign="top" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top" colspan="7" style="background:#ffffdd;" align="center"| '''Responsibility Matrix: | | valign="top" colspan="7" style="background:#ffffdd;" align="center"| '''<span id="RACI-Matrix-Service-Level-Management">Responsibility Matrix: ITIL Service Level Management</span>''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! width="50%" align="center" style="background:#ffffee;" | ITIL Role | Sub-Process | ! width="50%" align="center" style="background:#ffffee;" | ITIL Role | Sub-Process | ||
| Line 124: | Line 120: | ||
| align="left" |[[#Service Level Management Framework|Maintenance of the SLM Framework]] | | align="left" |[[#Service Level Management Framework|Maintenance of the SLM Framework]] | ||
| A[[Service Level Management#Accountable|<small>[1]</small>]]R[[Service Level Management#Responsible|<small>[2]</small>]] | | A[[Service Level Management#Accountable|<small>[1]</small>]]R[[Service Level Management#Responsible|<small>[2]</small>]] | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" |[[#Service Level Management Requirements|Identification of Service Requirements]] | | align="left" |[[#Service Level Management Requirements|Identification of Service Requirements]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| | | - | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R[[#ITIL Service Level Management Roles|<small>[4]</small>]] | | R[[#ITIL Service Level Management Roles|<small>[4]</small>]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 141: | Line 137: | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| R | | R | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" |[[#ITIL Service Level Management Reporting|Service Level Monitoring and Reporting]] | | align="left" |[[#ITIL Service Level Management Reporting|Service Level Monitoring and Reporting]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 164: | Line 160: | ||
<span id="Responsible">[2] ''R: Responsible'' according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Service Level Management.</span> | <span id="Responsible">[2] ''R: Responsible'' according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Service Level Management.</span> | ||
<span id="Team">[3] see [[Roles | <span id="Team">[3] see [[ITIL Roles|→ Role descriptions ...]]</span> | ||
<span id="ITIL Service Level Management Roles">[4] Capacity Manager, Availability Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, and Financial Manager. | <span id="ITIL Service Level Management Roles">[4] Capacity Manager, Availability Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, and Financial Manager (see [[ITIL Roles|→ Role descriptions ...]]) | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
<html><a rel="author" href="https://plus.google.com/111925560448291102517"><img style="margin:0px 0px 0px 0px;" src="/skins/Vector/images/itpm/bookmarking/gplus.png" width="16" height="16" title="By: Stefan Kempter | Profile on Google+" alt="Author: Stefan Kempter, IT Process Maps GbR" /></a></html> | |||
Revision as of 10:54, 30 June 2013
<seo metakeywords="itil service level management, itil slm, service level management, itil slm process, itil service level management process" metadescription="Service Level Management: ITIL process definition - Sub-processes - Terms - Additional information on Service Level Management." />

Overview
Objective: ITIL Service Level Management aims to negotiate Service Level Agreements with the customers and to design services in accordance with the agreed service level targets. Service Level Management is also responsible for ensuring that all Operational Level Agreements and Underpinning Contracts are appropriate, and to monitor and report on service levels.
Part of: Service Design
Process Owner: Service Level Manager
Process Description
Service Level Management has been completely redesigned in ITIL 2011 following the introduction of the Design Coordination process.
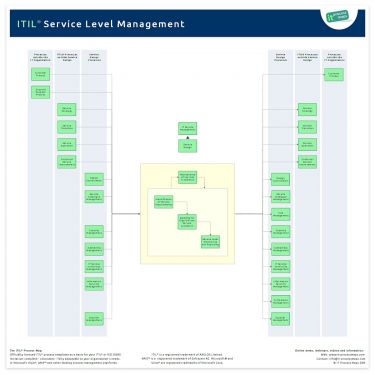
Coordinating activities have been removed.
Service Level Management is now mainly responsible for gathering service requirements, as well as monitoring and reporting with regards to agreed service levels.
The process overview of Service Level Management (.JPG) is showing the most important interfaces (see Figure 1).
Sub-Processes
These are the Service Level Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
- Maintenance of the SLM Framework
- Process Objective: To design and maintain the underlying structure of the Customer Agreement Portfolio, and to provide templates for the various SLM documents.
- Identification of Service Requirements
- Process Objective: To capture desired outcomes (requirements from the customer viewpoint) for new services or major service modifications. The service requirements are to be documented and submitted to an initial evaluation, so that alternatives may be sought at an early stage for requirements which are not technically or economically feasible.
- Agreements Sign-Off and Service Activation
- Process Objective: To have all relevant contracts signed off after completion of Service Transition, and to check if Service Acceptance Criteria are fulfilled. In particular, this process makes sure that all relevant OLAs are signed off by their Service Owners, and that the SLA is signed off by the customer.
- Service Level Monitoring and Reporting
- Process Objective: To monitor achieved service levels and compare them with agreed service level targets ("Service Level Report"). This information is circulated to customers and all other relevant parties, as a basis for measures to improve service quality.
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in ITIL Service Level Management to represent process outputs and inputs:
- Customer Agreement Portfolio
- While the Service Catalogue holds a complete list of the services managed by the service provider, the Customer Agreement Portfolio contains all Service Agreements which provide the framework for delivering services to specific customers.
- Operational Level Agreement (OLA)
- An agreement between an IT service provider and another part of the same organization. An OLA supports the IT service provider's delivery of services to customers. The OLA defines the goods or services to be provided and the responsibilities of both parties. For example there could be an OLA - between the IT service provider and a procurement department to obtain hardware in agreed times - between the Service Desk and a support group to provide Incident resolution in agreed times (see also: ITIL Checklist SLA - OLA).
- Outline of Service Requirements
- The desired outcome of a service, stated in terms of required service functionality (utility) and service levels (warranty). Based on this information, detailed service requirements are specified during the Service Design stage.
- Service Acceptance Criteria (SAC)
- A set of criteria used for service acceptance testing to ensure that an IT service meets its functionality and quality requirements and that the service provider is ready to operate the new service when it has been deployed.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- An agreement between an IT service provider and a customer. The SLA describes the IT service, documents service level targets, and specifies the responsibilities of the IT service provider and the customer. A single SLA may cover multiple services or multiple customers (see also: ITIL Checklist SLA - OLA).
- Service Level Report
- The Service Level Report gives insight into a service provider's ability to deliver the agreed service quality. To this purpose, it compares the agreed and actually achieved service levels, and also includes information on the usage of services, ongoing measures for service improvement, and any exceptional events. A Service Level Report is issued by the service provider for its customers, IT management and other Service Management processes. A similar report is also created by an external service supplier to document its achieved service performance.
- Service Level Requirements (SLR)
- The Service Level Requirements document contains the requirements for a service from the client viewpoint, defining detailed service level targets, mutual responsibilities, and other requirements specific to a certain (group of) customers. As the service enters new stages of its life cycle, the SLR document evolves into a draft Service Level Agreement.
- SLM Document Templates
- Templates for the various documents used within Service Level Management, e.g. Service Level Requirements, Service Level Agreements, Operational Level Agreements, Underpinning Contracts, Service Acceptance Criteria, ...
Checklists | KPIs
Roles | Responsibilities
- Service Level Manager - Process Owner
- The Service Level Manager is responsible for negotiating Service Level Agreements and ensuring that these are met. He makes sure that all IT Service Management processes, Operational Level Agreements and Underpinning Contracts are appropriate for the agreed service level targets. The Service Level Manager also monitors and reports on service levels.
- Service Owner
- The Service Owner is responsible for delivering a particular service within the agreed service levels. Typically, he acts as the counterpart of the Service Level Manager when negotiating Operational Level Agreements (OLAs). Often, the Service Owner will lead a team of technical specialists or an internal support unit.
| Responsibility Matrix: ITIL Service Level Management | ||||||
| ITIL Role | Sub-Process | Service Level Manager | Service Owner | Business Relationship Manager[3] | Applications Analyst[3] | Technical Analyst[3] | Other roles involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maintenance of the SLM Framework | A[1]R[2] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Identification of Service Requirements | AR | - | R | R | R | R[4] |
| Agreements Sign-Off and Service Activation | AR | R | - | - | - | - |
| Service Level Monitoring and Reporting | AR | - | - | - | - | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Service Level Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within Service Level Management.
[3] see → Role descriptions ...
[4] Capacity Manager, Availability Manager, IT Service Continuity Manager, and Financial Manager (see → Role descriptions ...)






