Basic Ideas behind ITIL: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | <itpmch><title>Basic Ideas behind ITIL | IT Process Wiki</title> | ||
<meta name="keywords" content="itil basic, basic itil" /> | |||
<meta name="description" content="Basic Ideas behind ITIL. The two illustrations below highlight the main issues ITIL seeks to address: ..." /> | |||
</itpmch> | |||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:ITIL-Wiki-deutsch.jpg|right|Basic Ideas behind ITIL | Image:ITIL-Wiki-deutsch.jpg|right|Basic Ideas behind ITIL | ||
| Line 9: | Line 12: | ||
The two illustrations below highlight the main issues ITIL seeks to address: | The two illustrations below highlight the main issues ITIL seeks to address: | ||
<p> </p> | |||
==Traditional | ==Traditional setup of the IT organization== | ||
[[Image:traditional_setup_it_organisation.jpg|frame|right|Traditional Setup of the IT | [[Image:traditional_setup_it_organisation.jpg|frame|right|Traditional Setup of the IT Organization]] | ||
Traditionally, there are two separate channels for the communication between the IT | Traditionally, there are two separate channels for the communication between the IT organization and the client: Agreements concerning new applications or those to be altered are concluded between client and Application Development, whilst issues concerning operations are subsequently settled with the production personnel. | ||
This approach | This approach creates two serious sets of risks: | ||
* Operational requirements, ensuring the error-free running of an application, are insufficiently considered during the development phase. | * Operational requirements, ensuring the error-free running of an application, are insufficiently considered during the development phase. | ||
* IT Operations is not fully able to control the release of applications into the productive environment; this might cause unforeseen side effects. | * IT Operations is not fully able to control the release of applications into the productive environment; this might cause unforeseen side effects. | ||
<br style="clear:both;"/> | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
==Setup of the IT | ==Setup of the IT organization according to ITIL== | ||
[[Image:setup_it_organisation_itil.jpg|frame|right|Setup of the IT | [[Image:setup_it_organisation_itil.jpg|frame|right|Setup of the IT Organization according to ITIL]] | ||
An [[ITIL Implementation|implementation method based on ITIL]] has to resolve these particular problems by placing IT Service Management after Application Management and ICT Infrastructure Management: Thus, IT Service Management mediates between development and production on the side of the IT | An [[ITIL Implementation|implementation method based on ITIL]] has to resolve these particular problems by placing IT Service Management after Application Management and ICT Infrastructure Management: Thus, IT Service Management mediates between development and production on the side of the IT organization, and the client on the business-side. | ||
The activities in Application Development and IT Operations are now co-ordinated and all the communication with the clients is directed via one central channel. | The activities in Application Development and IT Operations are now co-ordinated and all the communication with the clients is directed via one central channel. | ||
<br style="clear:both;"/> | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
<p> </p> | |||
<!-- This page is assigned to the following categories: --> | <!-- This page is assigned to the following categories: --> | ||
[[Category:IT Infrastructure Library ITIL]] | [[Category:IT Infrastructure Library ITIL]] | ||
<!-- --- --> | <!-- --- --> | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 23 January 2012

The two illustrations below highlight the main issues ITIL seeks to address:
Traditional setup of the IT organization
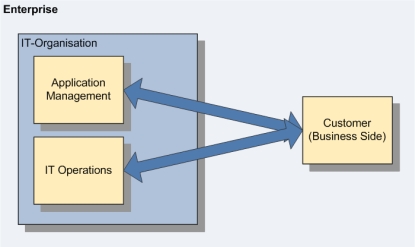
Traditionally, there are two separate channels for the communication between the IT organization and the client: Agreements concerning new applications or those to be altered are concluded between client and Application Development, whilst issues concerning operations are subsequently settled with the production personnel.
This approach creates two serious sets of risks:
- Operational requirements, ensuring the error-free running of an application, are insufficiently considered during the development phase.
- IT Operations is not fully able to control the release of applications into the productive environment; this might cause unforeseen side effects.
Setup of the IT organization according to ITIL
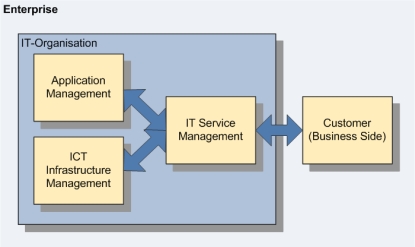
An implementation method based on ITIL has to resolve these particular problems by placing IT Service Management after Application Management and ICT Infrastructure Management: Thus, IT Service Management mediates between development and production on the side of the IT organization, and the client on the business-side.
The activities in Application Development and IT Operations are now co-ordinated and all the communication with the clients is directed via one central channel.






