Capacity Management: Difference between revisions
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
;<span id="Capacity Management Rules">Event Filtering and Correlation Rules</span> | ;<span id="Capacity Management Rules">Event Filtering and Correlation Rules</span> | ||
:Rules and criteria used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring systems. Some of those rules are defined during the Service Design stage, for example to ensure that Events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered. | :Rules and criteria used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring systems. Some of those rules are defined during the Service Design stage, for example to ensure that Events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered. | ||
: ''Note: The output "Event Filtering and Correlation Rules" has been added in ITIL 2011, to emphasize that (some) Event filtering and correlation rules should be designed by Capacity Management to support the detection of capacity issues.'' | |||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 99: | Line 100: | ||
| align="left" |[[#Business Capacity Management ITIL|Business Capacity Management]] | | align="left" |[[#Business Capacity Management ITIL|Business Capacity Management]] | ||
| A[[Capacity Management#Accountable|<small>[1]</small>]]R[[Capacity Management#Responsible|<small>[2]</small>]] | | A[[Capacity Management#Accountable|<small>[1]</small>]]R[[Capacity Management#Responsible|<small>[2]</small>]] | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" |[[#Service Capacity Management ITIL|Service Capacity Management]] | | align="left" |[[#Service Capacity Management ITIL|Service Capacity Management]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| R | | R | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" |[[#Component Capacity Management ITIL|Component Capacity Management]] | | align="left" |[[#Component Capacity Management ITIL|Component Capacity Management]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| | | - | ||
| R | | R | ||
| R | | R | ||
| Line 117: | Line 118: | ||
| align="left" |[[#Capacity Management Reporting|Capacity Management Reporting]] | | align="left" |[[#Capacity Management Reporting|Capacity Management Reporting]] | ||
| AR | | AR | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
| | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 12 April 2012
<seo metakeywords="itil capacity management, capacity management itil" metadescription="Capacity Management: ITIL process definition - Sub-processes - Terms - Additional information on ITIL Capacity Management." />

Overview
Objective: ITIL Capacity Management aims to ensure that the capacity of IT services and the IT infrastructure is able to deliver the agreed service level targets in a cost effective and timely manner. Capacity Management considers all resources required to deliver the IT service, and plans for short, medium and long term business requirements.
Part of: Service Design
Process Owner: Capacity Manager
Process Description
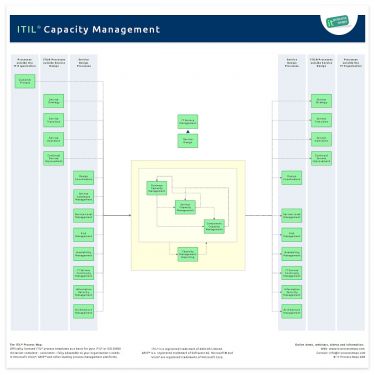
There are no major differences between Capacity Management in ITIL V3 (2007) and ITIL 2011.
Following the introduction of Design Coordination in ITIL 2011 the information flows have been adapted. The process overview of ITIL Capacity Management (.JPG) is showing the most important interfaces (see Figure 1).
Sub-Processes
These are the Capacity Management sub-processes and their process objectives:
- Business Capacity Management
- Process Objective: To translate business needs and plans into capacity and performance requirements for services and IT infrastructure, and to ensure that future capacity and performance needs can be fulfilled.
- Service Capacity Management
- Process Objective: To manage, control and predict the performance and capacity of operational services. This includes initiating proactive and reactive action to ensure that the performances and capacities of services meet their agreed targets.
- Component Capacity Management
- Process Objective: To manage, control and predict the performance, utilization and capacity of IT resources and individual IT components.
- Capacity Management Reporting
- Process Objective: To provide other Service Management processes and IT Management with information related to service and resource capacity, utilization and performance (see "Capacity Report").
Definitions
The following ITIL terms and acronyms (information objects) are used in ITIL Capacity Management to represent process outputs and inputs:
- Capacity Management Information System
- A virtual repository of all Capacity Management data, usually stored in multiple physical locations.
- Capacity Plan
- A Capacity Plan is used to manage the resources required to deliver IT services. The plan contains scenarios for different predictions of business demand, and costed options to deliver the agreed service level targets. (see: ITIL Checklist Capacity Plan)
- Capacity Report
- The Capacity Report provides other Service Management processes and IT Management with information related to service and resource utilization and performance.
- Event Filtering and Correlation Rules
- Rules and criteria used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring systems. Some of those rules are defined during the Service Design stage, for example to ensure that Events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered.
- Note: The output "Event Filtering and Correlation Rules" has been added in ITIL 2011, to emphasize that (some) Event filtering and correlation rules should be designed by Capacity Management to support the detection of capacity issues.
Checklists | KPIs
Roles | Responsibilities
- Capacity Manager - Process Owner
- The Capacity Manager is responsible for ensuring that services and infrastructure are able to deliver the agreed capacity and performance targets in a cost effective and timely manner.
- He considers all resources required to deliver the service, and plans for short, medium and long term business requirements.
| Responsibility Matrix: ITIL Capacity Management | ||||
| ITIL Role | Sub-Process | Capacity Manager | Service Owner[3] | Applications Analyst[3] | Technical Analyst[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Capacity Management | A[1]R[2] | - | - | - |
| Service Capacity Management | AR | R | - | - |
| Component Capacity Management | AR | - | R | R |
| Capacity Management Reporting | AR | - | - | - |
Remarks
[1] A: Accountable according to the RACI Model: Those who are ultimately accountable for the correct and thorough completion of the Capacity Management process.
[2] R: Responsible according to the RACI Model: Those who do the work to achieve a task within ITIL Capacity Management.
[3] see → Role descriptions ...






